Health Library
RAD-140 (Testolone)
Author: Dr. George Shanlikian, M.D. | Last Updated: May 23rd, 2025
- Home
- >
- Health Library
- >
- RAD-140 (Testolone)
Peptides
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
Potential Health Benefits of RAD-140
RAD-140 benefits include increased lean muscle mass, enhanced strength, and improved endurance, making it popular among athletes and bodybuilders. It may also support fat loss and promote faster muscle recovery without the side effects commonly associated with anabolic steroids.
- Improves muscle mass and strength [1-3]
- Fights cancer [4-6]
- Improves brain health [7-12]
- Promotes weight loss [14]
- Improves sexual health [15-18]
- Treats benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) [19-20]
- Improves bone health [21-23]
Key Takeaways
- Muscle Growth and Strength: RAD-140 is known to promote significant increases in lean muscle mass and strength, making it popular among bodybuilders and athletes.
- Enhanced Endurance: Users report improved stamina and physical performance, allowing for more intense and prolonged workouts.
- Fat Loss Support: RAD-140 may help reduce body fat while preserving muscle, contributing to a leaner physique.
- Selective Action: As a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), RAD-140 targets muscle and bone tissues, minimizing the side effects typically associated with anabolic steroids.
- Potential Neuroprotective Effects: Early research suggests RAD-140 may offer neuroprotective benefits, potentially supporting brain health and cognitive function.
What is RAD-140?
RAD-140, also known as Testolone, is a compound that belongs to the class of molecules called selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs). Unlike anabolic androgenic steroids, this orally ingestible product is non-steroidal in nature, which means that it has anabolic effects (e.g., increased muscle mass and strength, and accelerated bone growth) with almost zero side effects. This is because RAD-140 interacts only with androgenic receptors of the muscles and bones, but it doesn’t activate these receptors in other body parts.
How RAD-140 Works
RAD-140 works by allowing its molecules to bind to androgen receptors in the body. This, in turn, sends signals to the body, resulting in muscle build-up. This mechanism of action is similar to anabolic steroids. However, RAD-140 binds to androgen receptors only in bone and muscle tissue, making it a potential option for addressing muscle loss related to ageing and chronic diseases while decreasing the side effects.
Chemical Structure of RAD-140 (Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator)
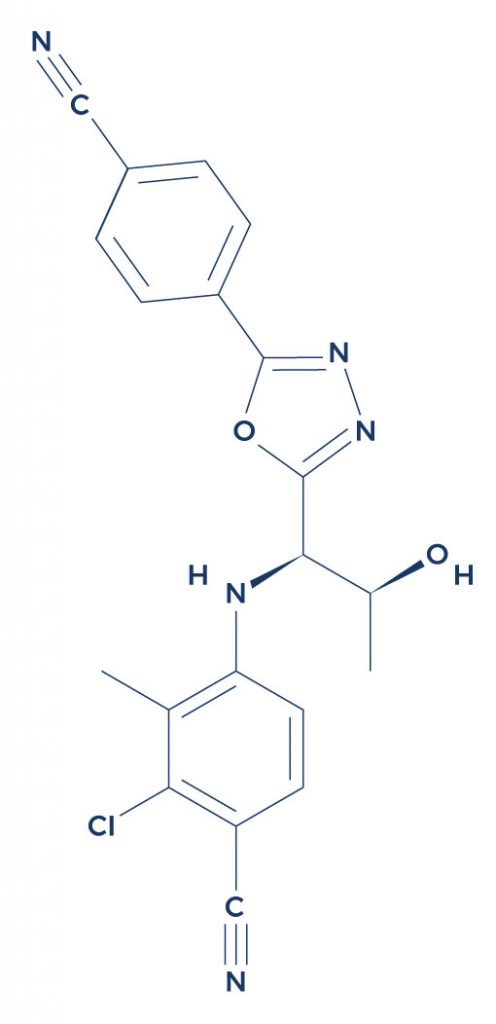
Research on RAD-140
A. Improves Muscle Mass and Strength

RAD-140 improves muscle mass and strength by selectively binding to androgen receptors in muscle and bone tissues, stimulating anabolic activity without affecting other organs. This targeted action promotes rapid muscle growth, enhances protein synthesis, and increases nitrogen retention, which are essential for building and maintaining lean muscle. Users often experience significant gains in strength, allowing for more intense training sessions and faster recovery times. Unlike traditional steroids, RAD-140 offers these benefits with a reduced risk of androgenic side effects, making it a popular choice for those seeking to improve performance and body composition.
- In patients with severe diseases (cancer, AIDS, and multiple sclerosis) that cause muscle wasting, RAD-140 treatment led to weight gain and increased bone and muscle cell growth. [1]
- In bodybuilders, RAD-140 administration increased muscle mass, decreased fat tissue, and improved stamina and endurance during high-intensity interval training. [2]
- In animals, RAD-140 administration appears to increase lean muscle mass. [3]
B. Fights Cancer
RAD-140 may help fight cancer by targeting androgen receptors found in certain cancer cells, particularly in breast cancer. Research suggests that RAD-140 can inhibit the growth of androgen receptor-positive breast cancer cells by blocking their ability to multiply. Unlike traditional hormone therapies, RAD-140 selectively activates androgen receptors in muscle and bone tissue while minimizing effects on other organs. This selective action may reduce cancer cell proliferation without the severe side effects associated with conventional treatments. Although promising, further clinical studies are needed to confirm its safety and effectiveness in cancer therapy.
- In patients with breast cancer, RAD-140 treatment suppressed the growth of cancer cells by blocking the effects of estrogen on tissues. [4-5]
- RAD-140 prevented the production of a protein called estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1), which is known to fuel cancer growth. [6]
C. Improves Brain Health

RAD-140 may improve brain health by exhibiting neuroprotective properties through its selective activation of androgen receptors in the brain. This activation may help protect neurons from degeneration and oxidative stress, which is particularly beneficial in conditions linked to cognitive decline, such as Alzheimer’s disease. Preclinical studies suggest that RAD-140 may enhance brain cell survival and reduce the impact of neurotoxic environments. While these effects are promising, further human research is needed to fully understand its long-term impact on brain health.
- In rat models of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), RAD-140 administration protected the neurons and decreased the levels of amyloid beta, which are abnormal protein plaques and is considered a hallmark of AD. [7]
- RAD-140 mimics the activation of beneficial androgen pathways in the brain which leads to the growth and development of brain tissues, enhanced neuron communication, memory formation, and cell survival. [8-11]
- In rats, RAD-140 increased the survival of new neurons in the brain. [12]
D. Promotes Weight Loss

RAD-140 may promote weight loss by increasing lean muscle mass and boosting metabolic activity. As muscle tissue requires more energy to maintain, users often experience a rise in their basal metabolic rate (BMR), leading to greater calorie expenditure throughout the day. Additionally, RAD-140 can help preserve muscle during a calorie deficit, which is crucial for maintaining strength while losing fat. By enhancing endurance and physical performance, it allows for more intense workouts, further supporting fat loss. However, its effects on weight loss are indirect and depend on diet and exercise habits.
- Supplementing with RAD-140 can lead to a dramatic fat loss over time. This is because RAD-140 can indirectly decrease fat tissue by increasing muscle mass. This effect also lowers circulating fat molecules known as low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which is implicated in obesity. [13] In addition, having higher levels of muscle mass increases the body’s metabolism, which ultimately leads to weight loss. [14]
E. Improves Sexual Health
RAD-140 may improve sexual health indirectly by increasing testosterone-like activity in the body, which can enhance libido, sexual performance, and overall vitality. Its anabolic properties may also boost energy levels, muscle mass, and confidence, all of which can contribute to a healthier sex drive. However, since RAD-140 suppresses natural testosterone production during use, these benefits may diminish without proper post-cycle therapy (PCT) to restore hormonal balance.
- In rats, SARMs enhanced the sexual preference of females for males but only if females had previous sexual experience. [15]
- In women, SARMs enhanced and stimulated libido and other parameters of sexuality. [16]
- In female rats that had undergone surgical removal of the ovaries, SARMs increased sexual motivation, with potency and efficacy comparable with testosterone propionate. [17]
- In male rats, SARMs improved various sexual parameters such as mounts, intromissions, ejaculations, and copulation efficiency. [18]
F. Treats Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
RAD-140 may help manage benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by selectively targeting androgen receptors in muscle and bone tissue without significantly stimulating the prostate. Unlike traditional anabolic steroids or testosterone, which can enlarge the prostate, RAD-140’s selective action reduces androgenic effects on the prostate gland. This selective binding may limit prostate growth and potentially alleviate BPH symptoms. Although promising, more clinical research is needed to confirm RAD-140’s effectiveness and safety for treating BPH in humans.
- SARMs at varying doses (5, 10, and 25 mg/kg) decreased prostate weight and were equal in efficacy to finasteride, a medication used mainly to treat BPH. [19]
- Repeated treatment with SARMs decreased prostate weight just like flutamide, a medication for prostate cancer and BPH. [20]
G. Improves Bone Health
RAD-140 improves bone health by selectively binding to androgen receptors in bone tissue, which may enhance bone mineral density and strength. This selective activation mimics the effects of natural androgens, promoting bone growth without affecting other tissues. By stimulating bone-building processes, RAD-140 may help prevent bone loss, particularly in aging individuals or those experiencing hormonal deficiencies. Although research is still ongoing, early studies suggest RAD-140 could be beneficial for maintaining skeletal integrity and reducing the risk of fractures.
- In androgen-deficient rats, SARMs administration prevented bone loss and maintained bone quality by stimulating bone formation while inhibiting bone breakdown. [21]
- In men with late-onset hypogonadism (low levels of sex hormones), SARMs administration increased bone mineral density and strength just like testosterone replacement therapy. [22]
- In castrated male rats, SARMs administration led to a significantly larger increase in total body bone mineral density. [23]
RAD-140 Side Effects
RAD-140 side effects are very uncommon. There have been some side effects associated with the use of this drug, wherein the patient had one of the issues listed below at some point while being on RAD-140. However, these side effects weren’t confirmed to be associated with the treatment and could have been a coincidence and not related to the use of RAD-140. Despite this, it was listed as a side effect associated with RAD-140, even though these associated side effects are very uncommon.
Side effects associated with RAD-140 may include the following:
- Acne
- Aggression
- Hair loss
- Headache
- Hormonal disorder
- Nausea
RAD 140 vs MK 677
RAD-140 (Testolone) and MK-677 (Ibutamoren) are both popular in fitness and bodybuilding but serve different functions. RAD-140 is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) known for its powerful muscle-building effects, strength gains, and neuroprotective properties, making it ideal for lean muscle growth and performance enhancement. On the other hand, MK-677 is a growth hormone secretagogue that boosts natural growth hormone and IGF-1 levels, promoting muscle recovery, fat loss, better sleep, and increased appetite. While RAD-140 is favored for fast, dry muscle gains, MK-677 is often used for long-term muscle preservation and overall well-being. Some users combine them to maximize muscle growth, recovery, and strength.
Most evidence suggests that any fertility-related effects from RAD-140 are reversible with proper post-cycle therapy (PCT) to restore natural hormone levels. However, the lack of extensive human studies means the long-term risks remain unclear. Individuals concerned about fertility should approach RAD-140 with caution and consider consulting a healthcare professional before use.
RAD vs RAD 140
RAD-150 vs. RAD-140: Key Differences
RAD-150 and RAD-140 are both selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) known for promoting muscle growth and enhancing physical performance. The primary difference lies in their chemical structure—RAD-150 is an esterified version of RAD-140, which allows for a slower release and longer half-life in the body. This means RAD-150 may require less frequent dosing while providing sustained effects, whereas RAD-140 typically needs more consistent administration to maintain optimal results.
Performance and Benefits Comparison
Both compounds are valued for their ability to increase lean muscle mass, strength, and endurance while aiding in fat loss. RAD-150’s extended half-life may lead to a more gradual and steady release, potentially reducing the risk of hormonal fluctuations. On the other hand, RAD-140 is known for delivering quicker results due to its faster absorption. Users of both SARMs report improved recovery times and enhanced athletic performance, but RAD-150’s longer activity window may be preferable for those seeking a more consistent anabolic effect.
Side Effects and Considerations
While both RAD-150 and RAD-140 are designed to target muscle and bone tissues selectively, they may still cause side effects such as hormonal suppression, mood changes, or mild liver stress. RAD-150’s esterified form could result in smoother effects and fewer side effects related to hormone spikes, while RAD-140’s quicker action may increase the likelihood of short-term hormonal imbalances. As with any SARM, responsible use, proper post-cycle therapy (PCT), and regular health monitoring are essential to minimize risks.
LGD 4033 vs RAD 140
LGD-4033 vs RAD-140: Muscle Growth and Strength
Both LGD-4033 (Ligandrol) and RAD-140 (Testolone) are popular selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) known for enhancing muscle growth and strength. LGD-4033 is often favored for gradual, steady gains in lean muscle mass, making it ideal for beginners or those seeking moderate muscle development. In contrast, RAD-140 is recognized for delivering faster, more substantial muscle gains and increased strength, which appeals to experienced users aiming for significant performance improvements.
Side Effects and Safety
While both compounds are designed to selectively target muscle and bone tissues, they carry potential side effects. LGD-4033 is generally considered milder, with a lower risk of hormonal suppression and minimal androgenic effects. RAD-140, however, is more potent and may cause more pronounced testosterone suppression and mood changes. Post-cycle therapy (PCT) is typically recommended after using either SARM to help restore natural hormone levels.
Best Use Cases
LGD-4033 is ideal for those seeking a balanced approach to muscle building with fewer side effects, making it suitable for longer cycles and beginners. On the other hand, RAD-140 is better suited for advanced users focused on maximizing muscle mass and strength in a shorter timeframe. The choice between the two depends on individual goals, experience level, and tolerance for potential side effects.
FAQ
Does RAD140 ruin testosterone?
RAD140 can suppress natural testosterone production during and after use, but it typically does not cause permanent damage if proper post-cycle therapy (PCT) is followed. However, testosterone suppression is a probable adverse drug reaction associated with RAD140 use, especially among bodybuilding enthusiasts seeking muscle gains.
What does RAD140 do to your brain?
Preliminary research suggests RAD140 may have neuroprotective properties, potentially protecting brain cells from degeneration. Unlike anabolic androgenic steroids, it selectively targets androgen receptors, reducing unwanted side effects. In the context of body building, RAD140 is favored for its ability to enhance muscle growth while minimizing adverse effects. However, long-term effects on the brain in humans remain unclear.
Is RAD140 hard on the liver?
RAD140 may cause mild liver stress, but severe liver damage is uncommon with responsible use. Regular liver function monitoring is recommended during a cycle, especially for individuals concerned about ageing, chronic diseases, and the impact of nutritional supplements on overall liver health. Medical research suggests that proper dosage and monitoring can help mitigate potential liver-related risks.
Is RAD140 bad for the kidneys?
There is limited evidence suggesting RAD140 directly harms the kidneys, but improper use, dehydration, or extended cycles could increase the risk of kidney strain and may lead to an adverse reaction, according to findings from the toxicology research group. Additionally, hepatic safety is a concern, as prolonged use may place stress on the liver.
What does RAD140 do to the brain?
RAD140 may promote neuroprotection by stimulating androgen receptors in the brain, potentially safeguarding against cognitive decline. However, past or present use of RAD140 could pose risks, including acute liver failure, especially with prolonged or high-dose cycles. Blood investigations are recommended to monitor liver function and overall health during and after use. More research is needed for definitive conclusions.
Does RAD140 increase testosterone?
No, RAD140 does not increase natural testosterone. Instead, it suppresses testosterone production during use, which, if unmanaged, could contribute to conditions like acute liver failure. Patient’s laboratory reports are essential for monitoring hormone levels and liver function, and post-cycle therapy is required for hormonal recovery.
Is RAD140 bad for your liver?
RAD140 can cause liver strain if used improperly or for extended periods, though it is not as hepatotoxic as anabolic steroids. It is sometimes researched for its potential to combat muscle-wasting diseases. In some cases, it may contribute to acute liver injury or induced jaundice, making regular health monitoring advisable.
Is RAD140 bad for your kidneys?
RAD140 is not directly linked to kidney damage, but using it irresponsibly can increase the risk of kidney stress, especially if hydration and dosage are not managed properly. Individuals with a known family history of autoimmune liver disease, viral hepatitis, or other pre-existing conditions should exercise caution and consult a healthcare professional before use.
Does RAD140 affect testosterone?
Yes, RAD140 suppresses natural testosterone production while in use. Without post-cycle therapy, testosterone levels may take time to return to normal, and an adverse drug reaction could occur if the body struggles to restore hormonal balance. Additionally, other liver biochemistry results may indicate stress or dysfunction during RAD140 use, highlighting the importance of regular health monitoring.
Does RAD140 cause gyno?
RAD140 is not known to directly cause gynecomastia (gyno) due to its selective action. However, hormonal imbalances from testosterone suppression may increase the risk, and changes in liver biochemistry could further contribute to hormonal disruptions, especially in individuals with an autoimmune disease. Additionally, RAD140 may exert anabolic effects on muscle tissue, which can influence hormone levels and increase the likelihood of hormonal imbalances.
Will RAD140 show up on a drug test?
Yes, RAD140 can be detected on specialized sports drug tests, particularly those used by organizations that screen for performance-enhancing drugs, monitor liver biochemistry for potential health risks, and investigate symptoms like abdominal pain.
Does RAD140 cause liver damage?
There is a potential for mild liver toxicity with RAD140, especially when used in high doses or over long periods. Monitoring liver biochemistry and liver enzymes during use is recommended, particularly for individuals aiming to increase lean body mass. In clinical pharmacology, regular assessments of liver function are crucial to detect early signs of hepatotoxicity and ensure safe usage.
What is better than MK-677?
It depends on your goals—RAD140 is better for muscle growth and strength, while other SARMs like LGD-4033 or YK-11 may offer faster muscle gains or different anabolic effects. Additionally, RAD140 may help combat muscle wasting, making it a potential option for those seeking to preserve lean muscle mass. Regular monitoring of total serum bilirubin concentration is recommended during RAD140 use to assess liver health and detect potential side effects.
Does RAD140 damage the liver?
While not as toxic as traditional steroids, RAD140 can cause mild to moderate liver stress, especially with long-term use or high dosages, increasing the risk of severe cholestatic liver injury and drug-induced liver injury. Monitoring total serum bilirubin concentration can help assess liver function and detect early signs of liver damage.
Does MK-677 increase bone size?
MK-677 may improve bone density over time by stimulating growth hormone and IGF-1 production, but it does not significantly increase overall bone size. Monitoring total serum bilirubin concentration is important, as improper use of MK-677 could pose risks, including severe liver injury in rare cases due to associated hepatotoxicity.
Does RAD140 lower testosterone?
Yes, RAD140 suppresses natural testosterone production during a cycle and may lower levels post-cycle without proper recovery protocols, though it is generally considered less suppressive than traditional anabolic androgenic steroids. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to assess potential liver damage from prolonged or high-dose use. Some users also explore herbal supplements to support liver health and hormone recovery during and after a cycle.
What are the long-term side effects of RAD140?
Long-term side effects are not fully understood but may include hormonal imbalance, liver strain, cardiovascular issues, bile acid concentration changes, chronic hepatitis, serious adverse events, and potential suppression of natural testosterone production.
What do SARMs do to your hormones?
SARMs selectively bind to androgen receptors, influencing hormone levels by increasing muscle growth while suppressing natural testosterone during and after use, similar to anabolic androgenic steroids nandrolone in their muscle-building effects but with potentially fewer side effects. Blood tests can help monitor hormone levels and detect any adverse effects during SARM use. However, some supplements included substances unapproved by regulatory agencies, raising concerns about safety and long-term health impacts.
Is RAD140 toxic to the liver?
RAD140 may cause mild liver toxicity, particularly with prolonged use, though it is generally less toxic than traditional anabolic steroids. In cases of recreational and athletic use, severe liver damage, including mild focal lobular inflammation, may occur. A liver transplant may be required in extreme cases, although this is rare with responsible use.
What does RAD140 do to the body?
RAD140 enhances muscle growth, increases strength, supports fat loss, and may provide neuroprotective benefits. It also suppresses natural testosterone production and may have potentially immune-mediated effects. Medical research council grants have supported studies investigating its effects on muscle and bone health, though concerns about severe hepatotoxicity have been raised with prolonged or high-dose use.
How bad is RAD140 for the liver?
When used responsibly, RAD140 poses minimal liver toxicity, but improper dosing or prolonged use can elevate liver enzymes and increase health risks. For a clinical pharmacology trainee participant, it is essential to take a thorough drug history before use to identify potential interactions and minimize risks, especially for those involved in body building who may combine it with other supplements or performance enhancers.
Does RAD140 decrease testosterone?
Yes, RAD140 suppresses testosterone production during and after use, making post-cycle therapy essential to restore hormone balance and prevent complications related to other liver disease, especially for those involved in body building.
How long does LGD-4033 stay in your system?
LGD-4033 has a half-life of approximately 24-36 hours and can remain detectable in the body for up to 5-6 weeks, depending on metabolism and dosage. Its preclinical and clinical development has provided insights into its pharmacokinetics and potential therapeutic applications, especially in body building for promoting muscle growth and recovery.
Reference
Bhasin S, Jasuja R. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) as Function Promoting Therapies. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care. 2009;12(3):232-240. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e32832a3d79. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2907129/.
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) as Function Promoting Therapies
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are being developed to enhance muscle and bone health without adverse effects on the prostate or cardiovascular system. Unlike traditional steroids, nonsteroidal SARMs act as full agonists in muscle and bone while partially stimulating the prostate. Preclinical and early human trials show their potential to increase muscle and bone mass, making them promising anabolic therapies for aging, chronic diseases, frailty, and osteoporosis.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19357508/.Geyer H, Schänzer W, Thevis M. Anabolic agents: recent strategies for their detection and protection from inadvertent doping. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2014;48(10):820-826. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2014-093526. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4033149/.
Anabolic agents: recent strategies for their detection and protection from inadvertent doping. British Journal of Sports Medicine
Anti-doping strategies focus on detecting anabolic agents, including steroids and SARMs, through advanced testing methods like isotope ratio mass spectrometry and the athlete’s biological passport. These efforts have significantly increased the detection of doping violations while also identifying sources of inadvertent doping, such as contaminated supplements and food products. Protecting clean athletes involves education, research, and improved methods to distinguish intentional from unintentional doping.You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24632537/.Miller CP, Shomali M, Lyttle CR, et al.Design, Synthesis, and Preclinical Characterization of the Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (SARM) RAD140. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2011;2(2):124-129. doi:10.1021/ml1002508. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4018048/.
Design, Synthesis, and Preclinical Characterization of the Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (SARM) RAD140
This report describes the discovery of RAD140, a potent, orally bioavailable, nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). The characterization of RAD140 in several preclinical models of anabolic androgen action is also described.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24900290/.Yu Z, He S, Wang D. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Inhibits the Growth of Androgen/Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Models with a Distinct Mechanism of Action. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2017; 23(24):7608-7620. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28974548.
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Inhibits the Growth of Androgen/Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Models with a Distinct Mechanism of Action
RAD140 is a potent androgen receptor (AR) agonist that selectively inhibits the growth of AR/ER+ breast cancer cells by suppressing the estrogen receptor (ER) pathway. Preclinical studies showed that RAD140 effectively reduced tumor growth in patient-derived xenografts (PDX) and demonstrated enhanced efficacy when combined with palbociclib. These findings support further clinical investigation of RAD140 as a potential treatment for AR/ER+ breast cancer.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28974548/Ziyang Yu, Suqin He, Jeffrey Brown, Chris Miller, Jamal Saeh, Gary Hattersley. RAD140, an orally available selective androgen receptor modulator, inhibits the growth of AR/ER positive breast cancer cell line- and patient-derived xenograft models [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2017; 2017 Apr 1-5; Washington, DC. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res 2017;77(13 Suppl):Abstract nr 3608. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2017-3608. Retrieved from http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/77/13_Supplement/3608.
RAD140, an orally available selective androgen receptor modulator, inhibits the growth of AR/ER positive breast cancer cell line- and patient-derived xenograft models [abstract]
RAD140, a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), demonstrated significant anti-tumor activity in AR/ER+ breast cancer models by inhibiting tumor growth, surpassing the efficacy of fulvestrant. It acted as a potent androgen receptor (AR) agonist in breast cancer cells while showing tissue selectivity by not activating AR in prostate cancer cells. Additionally, combining RAD140 with CDK4/6 or mTOR inhibitors further enhanced its anti-tumor effects, highlighting its potential as a targeted therapy for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/77/13_Supplement/3608/619400/.Yu Z, He S, Wang D. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Inhibits the Growth of Androgen/Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Models with a Distinct Mechanism of Action. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2017; 23(24):7608-7620. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28974548.
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Inhibits the Growth of Androgen/Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Models with a Distinct Mechanism of Action
RAD140 is a potent AR agonist that selectively targets AR/ER+ breast cancer cells, inhibiting tumor growth by repressing the ESR1 gene and ER pathway. Preclinical studies show that RAD140 effectively reduces tumor size in patient-derived xenografts (PDX) and enhances efficacy when combined with palbociclib. These findings support further clinical investigation of RAD140 as a potential treatment for AR/ER+ breast cancer.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28974548/.Jayaraman A, Christensen A, Moser VA, et al. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Is Neuroprotective in Cultured Neurons and Kainate-Lesioned Male Rats. Endocrinology. 2014;155(4):1398-1406. doi:10.1210/en.2013-1725. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3959610/.
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Is Neuroprotective in Cultured Neurons and Kainate-Lesioned Male Rats
RAD140, a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), provides neuroprotection in cultured neurons and male rat brains, similar to testosterone, without significantly affecting the prostate. Its protective effects rely on MAPK signaling and were demonstrated in vivo using a kainate lesion model, suggesting potential benefits for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24428527/.Bajetto A, Barbero S, Bonavia R, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α induces astrocyte proliferation through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 pathway. J Neurochem. 2001;77:1226–1236. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11389173.
Stromal cell-derived factor-1α induces astrocyte proliferation through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 pathway
SDF-1α, the ligand for CXCR4, stimulates the proliferation of rat type-I cortical astrocytes by activating ERK1/2 signaling. This effect is mediated by a PTX-sensitive G-protein, phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase, and Pyk2. These findings suggest that CXCR4/SDF-1 plays a key role in glial proliferation, impacting brain development, reactive gliosis, and tumor formation.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11389173/.Qui MS, Green SH. PC12 cell neuronal differentiation is associated with prolonged p21ras activity and consequent prolonged ERK activity. Neuron. 1992;9:705–717. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1382473.
PC12 cell neuronal differentiation is associated with prolonged p21ras activity and consequent prolonged ERK activity
Oncogenic ras in PC12 cells induces neuronal differentiation through sustained activation of ERK proteins (p42erk2 and p44erk1), which act as primary downstream effectors. Growth factors like NGF and FGF maintain prolonged p21ras and ERK activation, promoting differentiation, while EGF, which only triggers transient activation, does not. This suggests that sustained ERK activity is essential for neuronal differentiation.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1382473/.Krapivinsky G, Krapivinsky L, Manasian Y, et al. The NMDA receptor is coupled to the ERK pathway by a direct interaction between NR2B and RasGRF1. Neuron. 2003;40:775–784. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14622581.
The NMDA receptor is coupled to the ERK pathway by a direct interaction between NR2B and RasGRF1
NR2B-containing NMDARs play a key role in activating the ERK pathway, which is essential for synaptic plasticity and memory. RasGRF1 specifically interacts with NR2B to regulate ERK activation, and disrupting this interaction impairs NMDAR-dependent ERK signaling in neurons.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14622581/.Alonso M, Viola H, Izquierdo I, Medina JH. Aversive experiences are associated with a rapid and transient activation of ERKs in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002;77:119–124. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11749089.
Aversive experiences are associated with a rapid and transient activation of ERKs in the rat hippocampus
Aversive experiences, such as inhibitory avoidance training or foot shocks, rapidly activate ERK/MAPK signaling in the hippocampus, suggesting a key role for these kinases in memory formation.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11749089/.Hamson DK, Wainwright SR, Taylor JR, Jones BA, Watson NV, Galea LA. Androgens increase survival of adult-born neurons in the dentate gyrus by an androgen receptor-dependent mechanism in male rats. Endocrinology. 2013; 154(9):3294-304. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23782943.
Androgens increase survival of adult-born neurons in the dentate gyrus by an androgen receptor-dependent mechanism in male rats
Androgens like testosterone and DHT promote hippocampal neurogenesis through androgen receptors (ARs), but not in the dentate gyrus. Studies in androgen-insensitive rats and AR-blocked models confirm that DHT enhances neuron survival via AR activation. These findings suggest androgens influence brain plasticity, potentially impacting neurodegenerative disorders.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23782943/.Kesaniemi YA, Grundy SM. Increased low density lipoprotein production associated with obesity. Arteriosclerosis (Dallas, Tex.). ; 3(2):170-7. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6838434.
Increased low density lipoprotein production associated with obesity
This study compared apoLDL turnover and cholesterol balance in six obese and six control men with similar cholesterol levels. Despite having similar LDL-cholesterol concentrations, obese patients showed significantly higher apoLDL production rates. This was explained by a larger plasma volume, increased breakdown of apoLDL, and higher protein-to-cholesterol ratios in LDL. The study concluded that obese individuals have an increased turnover of apoLDL, which may contribute to a higher risk of coronary heart disease.
You can read the abstract of this article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6838434.
McPherron AC, Guo T, Bond ND, Gavrilova O. Increasing muscle mass to improve metabolism. Adipocyte. 2013;2(2):92-98. doi:10.4161/adip.22500. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3661116/.
Increasing muscle mass to improve metabolism
Increasing skeletal muscle mass by inhibiting myostatin improves insulin sensitivity and prevents diabetes in a mouse model of lipodystrophy, suggesting a potential strategy for diabetes prevention and regulation of food intake.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23805405/.Kudwa AE, López FJ, McGivern RF, Handa RJ. A selective androgen receptor modulator enhances male-directed sexual preference, proceptive behavior, and lordosis behavior in sexually experienced, but not sexually naive, female rats. Endocrinology. 2010; 151(6):2659-68. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20392832.
A selective androgen receptor modulator enhances male-directed sexual preference, proceptive behavior, and lordosis behavior in sexually experienced, but not sexually naive, female rats
The study examined the effects of LGD-3303, a selective androgen receptor modulator, on female rats’ sexual behavior. Results showed that LGD-3303 enhanced male preference in sexually experienced females but reduced it in sexually naive ones. Additionally, it increased lordosis and proceptivity behaviors when combined with low-dose estrogen and progesterone, suggesting its potential as a treatment for female sexual desire disorders with fewer side effects than traditional androgens.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20392832/.Negro-Vilar A. Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs): a novel approach to androgen therapy for the new millennium. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 1999; 84(10):3459-62. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10522980.
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs): a novel approach to androgen therapy for the new millennium
No abstract available
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10522980/.Jones A, Hwang DJ, Duke CB. Nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators enhance female sexual motivation. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 2010; 334(2):439-48. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20444881.
Nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators enhance female sexual motivation
This study explores the effects of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) on bone density, muscle wasting, and female sexual motivation after menopause. Researchers synthesized and tested various SARM analogs, finding that structural modifications influenced androgenic and anabolic activity. In animal models, certain SARMs selectively promoted muscle growth while sparing prostate tissue and increased sexual motivation in ovariectomized rats, suggesting their potential as a targeted treatment for hypoactive sexual desire disorder without the side effects of traditional testosterone therapy.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20444881/.Miner JN, Chang W, Chapman MS. An orally active selective androgen receptor modulator is efficacious on bone, muscle, and sex function with reduced impact on prostate. Endocrinology. 2007; 148(1):363-73. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17023534.
An orally active selective androgen receptor modulator is efficacious on bone, muscle, and sex function with reduced impact on prostate
LGD2226 is a nonsteroidal, highly selective androgen receptor ligand that promotes muscle and bone growth while minimizing prostate-related side effects. It demonstrates strong anabolic activity in cell and animal models, enhancing bone strength and improving sexual function in male rats. These findings suggest that LGD2226 and similar selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) could be effective therapeutics for muscle, bone, and sexual health without the drawbacks of traditional androgens.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17023534/.Omwancha J, Brown TR. Selective androgen receptor modulators: in pursuit of tissue-selective androgens. Current opinion in investigational drugs (London, England : 2000). 2006; 7(10):873-81. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17086931.
Selective androgen receptor modulators: in pursuit of tissue-selective androgens
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are designed to enhance muscle and bone growth while minimizing androgenic effects, making them potential treatments for conditions like male hypogonadism, osteoporosis, muscle wasting, and prostate disorders.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17086931/.Nejishima H, Yamamoto N, Suzuki M, Furuya K, Nagata N, Yamada S. Anti-androgenic effects of S-40542, a novel non-steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Prostate. 2012; 72(14):1580-7. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22430536.
Anti-androgenic effects of S-40542, a novel non-steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
S-40542, a novel tetrahydroquinoline (THQ) derivative, was identified as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) antagonist with high AR binding affinity. It reduced prostate weight in normal and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) model rats while having minimal impact on muscle mass and hormone levels compared to flutamide. These findings suggest S-40542 may offer a prostate-selective therapeutic option for BPH and aid in developing safer SARM antagonists.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22430536/.Rosen J, Negro-Vilar A. Novel, non-steroidal, selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) with anabolic activity in bone and muscle and improved safety profile. Journal of musculoskeletal & neuronal interactions. 2002; 2(3):222-4. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15758439.
Novel, non-steroidal, selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) with anabolic activity in bone and muscle and improved safety profile
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), like LGD2226, show promise in treating osteoporosis by preventing bone loss and stimulating new bone formation without the side effects of traditional androgens. In studies using an androgen-deficient rat model, LGD2226 maintained bone quality, enhanced muscle growth, and suppressed bone turnover, suggesting its potential as a safer alternative for hormone replacement therapy in both men and women.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15758439/.Coss CC, Jones A, Hancock ML, Steiner MS, Dalton JT. Selective androgen receptor modulators for the treatment of late onset male hypogonadism. Asian Journal of Andrology. 2014;16(2):256-261. doi:10.4103/1008-682X.122339. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3955335/.
Selective androgen receptor modulators for the treatment of late onset male hypogonadism. Asian Journal of Andrology
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) show potential for treating late-onset male hypogonadism by providing anabolic benefits without androgenic side effects. However, regulatory clarity and long-term safety data are needed before they can be widely used as an alternative to existing testosterone therapies.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24407183/.Gao W, Reiser PJ, Coss CC, et al. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator Treatment Improves Muscle Strength and Body Composition and Prevents Bone Loss in Orchidectomized Rats. Endocrinology. 2005;146(11):4887-4897. doi:10.1210/en.2005-0572. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2039881/.
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator Treatment Improves Muscle Strength and Body Composition and Prevents Bone Loss in Orchidectomized Rats
S-4, a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), demonstrated strong anabolic effects in skeletal muscle, bone, and the pituitary of castrated male rats while minimizing androgenic activity in the prostate. It effectively restored muscle mass, strength, and bone mineral density, outperforming dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in bone benefits while causing significantly less prostate enlargement. These findings highlight the potential therapeutic advantages of SARMs over traditional steroidal androgens.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16099859/.
Patient Success Stories

Before
After

At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health.
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer

Before
After

I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics. Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old Actress (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
Free Consultation
Start Your Journey to a Younger, Healthier You!
Categories
Information
Free Consultation
STEPS AWAY FROM A YOUNGER. HEALTHIER YOU!
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have








