Peptides
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
- Potential Benefits of Zinc-Thymulin
- Key Takeaways
- What is Zinc-Thymulin?
- How Zinc-Thymulin Works
- Chemical Structure of Zinc-Thymulin
- Research on Zinc-Thymulin
- Zinc-Thymulin Side Effects
- What is Zinc Thymulin Peptide?
- What is Thymulin Hormone?
- Zinc Thymulin Supplement
- Zinc Thymulin for Hair Loss
- Zinc Thymulin for Hair Growth
- Zinc Thymulin Spray
- Zinc Thymulin Foam
- Topical Peptide Zinc Thymulin
- Zinc Thymulin and Hair Follicles
- FAQ
- Reference
Table of Contents
- Potential Benefits of Zinc-Thymulin
- Key Takeaways
- What is Zinc-Thymulin?
- How Zinc-Thymulin Works
- Chemical Structure of Zinc-Thymulin
- Research on Zinc-Thymulin
- Zinc-Thymulin Side Effects
- What is Zinc Thymulin Peptide?
- What is Thymulin Hormone?
- Zinc Thymulin Supplement
- Zinc Thymulin for Hair Loss
- Zinc Thymulin for Hair Growth
- Zinc Thymulin Spray
- Zinc Thymulin Foam
- Topical Peptide Zinc Thymulin
- Zinc Thymulin and Hair Follicles
- FAQ
- Reference
Overall Health Benefits of Zinc-Thymulin
Zinc-thymulin promotes hair regrowth, reduces inflammation, enhances skin repair, and supports immune modulation, making it a versatile option for managing hair loss, inflammatory skin conditions, and skin rejuvenation.
- Fights hair loss [1-2]
- Boosts immune function [3-6]
Key Takeaways
- Immune Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Zinc-thymulin is a peptide that mimics thymulin, a thymus-derived hormone, and combines it with zinc to regulate immune responses and reduce inflammation, making it valuable for skin and scalp health.
- Promotes Hair Regrowth: Topical zinc-thymulin has been shown to stimulate the anagen (growth) phase of hair follicles, making it a promising treatment for conditions like androgenetic alopecia.
- Skin Health and Repair: Zinc-thymulin enhances skin barrier function, reduces oxidative stress, and promotes cellular repair, helping to manage conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne while supporting overall skin rejuvenation.
- Cosmetic and Anti-Aging Applications: Due to its reparative and antioxidant properties, zinc-thymulin is gaining attention in the cosmetic industry as a potential solution to delay signs of skin aging and improve skin texture and resilience.
- Favorable Safety Profile: Clinical and cosmetic applications of zinc-thymulin are generally well-tolerated, but further research is needed to refine formulations, establish optimal dosages, and validate long-term effectiveness for broader dermatological use.
What is Zinc-Thymulin?
Zinc-Thymulin (ZT) is a spray solution commonly prescribed for the treatment of hair loss and bald patches on the scalp. It’s basically the combination of two natural compounds zinc and thymulin. Zinc is a nutrient involved in the regulation of immune function and metabolism while thymulin is a hormone involved in the development of T-lymphocytes into their fully-functional state.
How Zinc-Thymulin Works
Hair grows and becomes fuller because of the anagen phase. During this growth and development phase, the hair follicle causes the root of the hair to divide rapidly. Normally, the anagen phase is increased in younger individuals and gradually decreases with advancing age. Therefore, this age-related decline leads to weaker and thinner hair. To successfully treat hair loss, zinc-thymulin works by initiating the anagen phase. This important mechanism completely restores hair growth, resulting in fuller and healthier hair.
Chemical Structure of Zinc-Thymulin
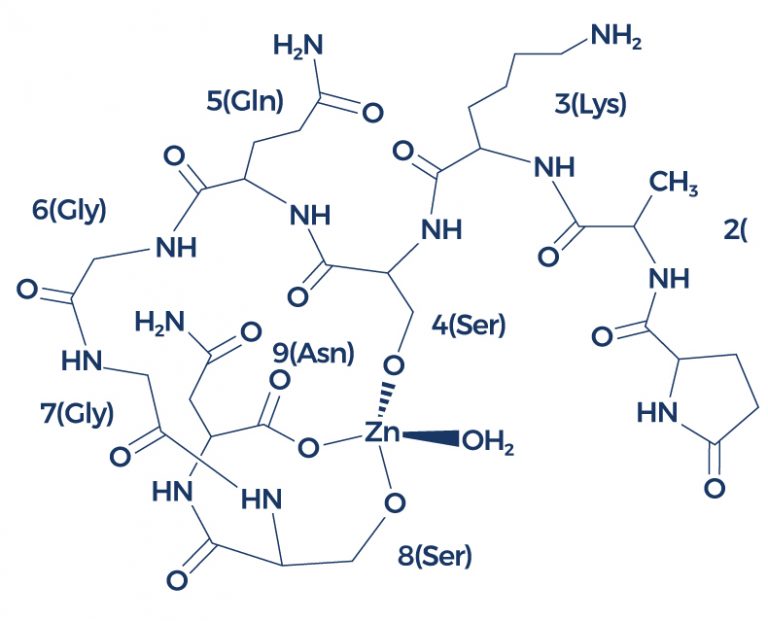
Research on Zinc-Thymulin
A. Fights Hair Loss

Older adults and even younger individuals in their early 20s can experience androgenetic alopecia, a genetic condition that can affect both genders. In men, it’s known as male pattern baldness and is characterized by a receding hairline from the crown and frontal scalp. In women, the condition is called female pattern baldness and is characterized by extensive hair loss at the crown.
A study by Vickers and colleagues investigated the safety and efficacy of the metallopeptide (an amino acid that contains metal ion) zinc-thymulin for treating androgenetic alopecia. [1] In this study, 18 adult subjects (17 males and 1 female) with an age range of 35-90 years and with a diagnosis of androgenetic alopecia were included. All subjects received a topical spray of zinc-thymulin on the scalp for 4-10 months. Baseline and after-treatment images of the scalp were taken in order to determine improvement in hair growth.
After 3,300 treatment days, zinc-thymulin produced no adverse effects or local side effects. Significant hair assessment improvement was observed in subjects who completed 6 months or more of continuous treatment. This was evidenced by a significant increase in the number of new hair growths, unlike in baseline where absent hair was noticeable in some regions of the scalp.
In a recent study by Meier and colleagues, it was found that zinc-thymulin increases human hair shaft production. [2] In this study, researchers treated hair follicles with zinc-thymulin and analyzed their hair cycle scores. Results showed that hair follicles treated with zinc-thymulin had a longer anagen phase compared with untreated hair follicles.
These findings suggest that topical application of zinc-thymulin is safe and effective for initiating and maintaining the anagen phase of the hair cycle, making it a potential therapeutic option for male and female pattern baldness.
B. Boosts Immune Function

Zinc-Thymulinis not just for hair regeneration. Evidence suggests that this powerful peptide also has beneficial effects on immune function.
In one study, Coto and colleagues found that zinc-thymulin stimulates nuclear protein kinase C in isolated lymphocyte nuclei. [3] Several lines of evidence suggest that nuclear protein kinase C is involved in the regulation of biological processes of the immune system such as immune cell proliferation and maturation, establishment and maintenance of cell polarity (spatial differences in shape, structure, and function within a cell), maintenance of the normal balance between T cells, and regulation of signaling pathways vital for both innate and adaptive immunity. [4-5]
In another study, Haddad investigated the effects of zinc-thymulin in an in vitro model of fetal alveolar type II epithelial cells (FATEII). [6] FATEII secretes a substance known as surfactant, which is important for lung function. Treatment of FATEII with zinc-thymulin resulted in an anti-inflammatory effect via inhibition of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) pathway. This suggests that zinc-thymulin may exert beneficial effects on immune function by suppressing the inflammatory process.
Zinc-Thymulin Side Effects
Zinc-Thymulin Side Effects Overview
Zinc-thymulin, a synthetic peptide composed of zinc and thymulin, is primarily researched for its potential role in hair regrowth, immune modulation, and anti-inflammatory effects. While generally considered safe in clinical studies, side effects can occur, especially if dosages exceed recommended levels or individual sensitivities are present. As with any peptide or therapeutic intervention, understanding potential adverse effects is crucial before use.
Common and Mild Side Effects
Most users of zinc-thymulin report minimal side effects when administered at appropriate dosages. Mild reactions such as localized redness, swelling, or irritation at the injection site are among the most common, often resolving within a few hours. Other minor side effects may include transient fatigue, headache, or slight nausea, which are generally short-lived and manageable without additional medical intervention.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
Rarely, zinc-thymulin may cause systemic reactions, particularly in individuals with pre-existing zinc sensitivity or autoimmune conditions. Allergic reactions, though uncommon, can manifest as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, requiring immediate medical attention. Overuse or improper administration could also disrupt zinc balance, leading to symptoms such as gastrointestinal distress or immune system suppression. To minimize risks, it is essential to use zinc-thymulin under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
What is Zinc Thymulin Peptide?
Zinc Thymulin is a synthetic peptide that combines the trace element zinc with thymulin, a thymic hormone primarily involved in immune system regulation. Thymulin, naturally produced by the thymus gland, plays a crucial role in the maturation and differentiation of T-cells, which are essential for adaptive immunity. When combined with zinc, the peptide becomes bioactive and exerts immunomodulatory effects, making it a subject of interest in research related to immune-related disorders and aging.
One of the key applications of Zinc Thymulin lies in its potential for promoting hair growth. Studies have indicated that it may stimulate hair follicle activity by modulating the immune system in a way that reduces inflammation and supports follicular health. This property has led to its exploration as a therapeutic agent for conditions like alopecia areata, a form of autoimmune hair loss. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory effects make it a candidate for other applications in dermatology and regenerative medicine.
Beyond its dermatological uses, Zinc Thymulin’s immune-enhancing properties hold promise in addressing age-related immune decline, commonly referred to as immunosenescence. By restoring T-cell function, it could help improve the body’s ability to fight infections and recover from injuries. While research into Zinc Thymulin is still in its early stages, its dual ability to modulate the immune system and support tissue regeneration positions it as a valuable molecule for therapeutic development.
What is Thymulin Hormone?
Thymulin is a peptide hormone secreted by the thymus gland, an organ located behind the sternum that plays a crucial role in the immune system, particularly during childhood. It is produced by thymic epithelial cells and primarily functions in the development and regulation of T-lymphocytes, which are essential for adaptive immunity. Thymulin also enhances the actions of natural killer cells, contributing to the body’s defense against infections and malignancies.
The activity of thymulin is closely tied to zinc levels in the body, as it requires zinc to remain biologically active. This hormone not only influences immune responses but also has neuroendocrine effects, linking the immune system with hormonal regulation. Research has shown that thymulin has anti-inflammatory properties and can modulate the release of various cytokines, making it an area of interest for understanding immune-related conditions and potential therapies.
With age, thymulin levels decline due to the involution of the thymus, which may contribute to the weakening of the immune system in older adults. This decline is associated with a reduced ability to fight infections and an increased risk of autoimmune diseases. As such, thymulin has been explored in research related to aging, immune dysfunction, and even conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, emphasizing its importance in maintaining overall health and immune resilience.
Zinc Thymulin Supplement
Zinc thymulin is a bioactive compound derived from the interaction of zinc ions and thymulin, a hormone produced by the thymus gland. This compound plays a significant role in the regulation of immune system activity, as thymulin is essential for the maturation and differentiation of T-cells. Zinc is a cofactor required for thymulin’s biological activity, and supplementation with zinc thymulin has been studied for its potential to enhance immune function, particularly in individuals with zinc deficiency or compromised immune systems.
Research into zinc thymulin supplementation suggests potential benefits in addressing immune dysfunction, reducing inflammation, and promoting skin health. Its anti-inflammatory properties have made it a candidate for managing conditions such as alopecia areata, where hair loss is linked to autoimmune activity. Additionally, zinc thymulin may help combat age-related declines in immune function, making it a promising therapeutic option for elderly populations or those with chronic illnesses that impair immunity.
Although zinc thymulin shows promise, it is not widely available as a standalone supplement and is primarily used in experimental or clinical settings. Its safety and efficacy for long-term use remain areas of ongoing research. Individuals considering zinc thymulin supplementation should consult with a healthcare provider, particularly if they have underlying health conditions or are on medications that may interact with zinc. Like any supplement, proper dosing and medical supervision are critical to ensure its benefits are maximized while minimizing potential risks.
Zinc Thymulin for Hair Loss
Zinc thymulin is a synthetic peptide composed of thymulin and zinc, developed for its potential role in addressing hair loss. Thymulin, a hormone naturally produced by the thymus gland, plays a key role in immune regulation, while zinc is essential for various biological processes, including cell growth and repair. Together, zinc thymulin has been found to exert anti-inflammatory effects and promote hair follicle health, making it a promising candidate for managing hair loss conditions such as androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata.
Research suggests that zinc thymulin may stimulate hair follicle activity by modulating the immune response and promoting the proliferation of dermal papilla cells, which are crucial for hair growth. In some studies, topical or injectable forms of zinc thymulin demonstrated potential to increase hair density and reduce hair thinning. Its effects appear to be particularly relevant for individuals whose hair loss is linked to inflammation or autoimmune conditions, as zinc thymulin may help counteract these underlying factors.
While the results of early studies are encouraging, zinc thymulin is not yet widely available as a treatment for hair loss and remains largely experimental. More robust clinical trials are needed to establish its efficacy, optimal dosing, and safety profile. For individuals considering this option, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss potential benefits, risks, and alternative treatments tailored to their specific condition.
Zinc Thymulin for Hair Growth
Zinc thymulin is a synthetic peptide that combines zinc with thymulin, a thymus gland-derived hormone. It has gained attention in recent years as a potential treatment for hair loss due to its role in hair follicle regulation. Zinc is essential for maintaining healthy hair follicles, while thymulin has immunomodulatory properties that may reduce inflammation and support hair growth. Together, they are believed to enhance follicle health and stimulate the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle.
Studies on zinc thymulin have demonstrated promising results, particularly in conditions like androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata. The peptide appears to work by modulating inflammatory responses and promoting the proliferation of dermal papilla cells, which play a crucial role in hair follicle development. Unlike some hair loss treatments, zinc thymulin is non-hormonal, making it a potential option for individuals seeking alternative therapies with fewer systemic side effects.
Zinc thymulin is typically administered topically to target the scalp directly, ensuring better absorption and minimizing systemic exposure. While initial research is encouraging, more extensive clinical trials are needed to establish its efficacy, optimal dosage, and long-term safety. As interest grows, zinc thymulin could become an innovative addition to the arsenal of treatments available for individuals battling hair loss.
Zinc Thymulin Spray
Zinc thymulin spray is a topical or nasal formulation combining zinc, an essential trace element, with thymulin, a thymic peptide involved in immune regulation. This combination is primarily researched for its potential to improve hair regrowth in conditions like alopecia areata. Zinc plays a critical role in cellular function, enzyme activity, and immune support, while thymulin modulates the activity of T-cells and other immune responses. Together, they may synergistically stimulate hair follicles and reduce inflammation contributing to hair loss.
The mechanism of zinc thymulin spray is based on its dual action. Zinc enhances thymulin’s biological activity and stabilizes its molecular structure. When applied topically or via a nasal spray, the combination is thought to stimulate hair follicle activity by promoting keratinocyte proliferation and reducing local inflammation. Additionally, it may support hair follicle cycling from the telogen (resting) phase back into the anagen (growth) phase. This dual mechanism makes it a promising candidate for non-invasive hair regrowth therapy.
Although zinc thymulin spray is still under investigation, preliminary studies suggest its potential in addressing autoimmune-related and non-scarring hair loss. Its ease of application and favorable safety profile make it appealing as an alternative to more invasive or systemic treatments. However, broader clinical trials are necessary to confirm its efficacy, optimal dosage, and long-term safety. Beyond hair loss, researchers are exploring its role in immune modulation and wound healing, though these areas require further validation.
Zinc Thymulin Foam
Zinc thymulin foam is a topical formulation combining zinc, an essential mineral, and thymulin, a hormone derived from the thymus gland. This combination has garnered interest for its potential role in skin and hair health due to its anti-inflammatory, immune-modulating, and regenerative properties. When applied to the skin, zinc thymulin foam may help improve conditions like alopecia, acne, or eczema by promoting healthier hair follicles and reducing localized inflammation.
The primary mechanism behind zinc thymulin foam lies in the synergistic action of its components. Zinc is well-known for its role in wound healing, cell proliferation, and immune system regulation. Thymulin, on the other hand, enhances T-cell function and has been shown to regulate inflammatory responses. Together, they can support hair follicle activity and potentially stimulate hair growth while maintaining a healthy scalp environment.
This formulation is typically prescribed in clinical settings for patients experiencing hair loss or inflammatory skin conditions, often as part of a broader treatment plan. The foam’s easy application and targeted delivery make it a practical option for long-term use. While promising, more research is needed to fully validate its efficacy and safety across diverse populations and dermatological concerns.
Topical Peptide Zinc Thymulin
Zinc thymulin is a synthetic peptide that mimics the natural thymulin hormone produced by the thymus gland. It plays a crucial role in immune modulation and anti-inflammatory processes. When formulated as a topical solution, zinc thymulin combines the benefits of zinc, a vital trace element for skin health, and thymulin, known for its ability to regulate the activity of T-cells in the immune system. This unique blend has garnered attention in dermatological and cosmetic applications due to its potential to rejuvenate skin and address inflammatory skin conditions.
One of the most prominent uses of topical zinc thymulin is in promoting hair regrowth and combating hair loss conditions like androgenetic alopecia. Research suggests that zinc thymulin stimulates the hair follicle’s anagen (growth) phase while reducing inflammation in the scalp, which often accompanies hair loss. Furthermore, the peptide’s anti-inflammatory properties make it beneficial in managing skin disorders such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne. Its ability to restore skin barrier function and enhance cellular repair contributes to healthier and more resilient skin.
Zinc thymulin’s topical formulation is generally well-tolerated, with a favorable safety profile in clinical and cosmetic use. As interest in peptide-based therapies grows, zinc thymulin is being explored for its potential to prevent oxidative stress, improve wound healing, and delay signs of skin aging. Its mechanism of action—combining immune regulation with the reparative benefits of zinc—positions it as a promising option for a variety of dermatological and cosmetic concerns. However, further clinical studies are needed to establish optimal concentrations, long-term efficacy, and broader applications.
Zinc Thymulin and Hair Follicles
Zinc-Thymulin is a bioactive peptide complex that plays a significant role in hair follicle regeneration and growth. It is composed of thymulin, a thymic peptide involved in immune modulation, and zinc, an essential mineral for cellular function. Research suggests that Zinc-Thymulin helps extend the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle by stimulating follicular activity and reducing inflammation. As people age, the anagen phase shortens, leading to thinner, weaker hair. By reactivating dormant follicles and promoting cell proliferation, Zinc-Thymulin has gained attention as a potential treatment for hair loss conditions such as androgenetic alopecia.
Hair follicles undergo a continuous cycle of growth (anagen), regression (catagen), and rest (telogen). Zinc-Thymulin primarily influences the anagen phase by enhancing the signaling pathways responsible for follicle regeneration. This complex is believed to activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling, a crucial pathway for hair growth and follicle stem cell activation. Additionally, Zinc-Thymulin has been found to reduce inflammation in the scalp, which is often linked to hair thinning and shedding. By creating a more favorable environment for follicular activity, it supports thicker, healthier hair growth while potentially slowing down hair loss progression.
One of the advantages of Zinc-Thymulin as a hair loss treatment is its lack of hormonal interference. Unlike medications such as finasteride, which inhibit dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and can cause hormonal side effects, Zinc-Thymulin works through a different mechanism that does not disrupt endocrine function. This makes it a promising option for individuals looking for a safer, non-hormonal approach to hair restoration. However, its effectiveness may vary depending on individual factors, and further clinical studies are needed to determine optimal dosages and long-term benefits. Despite this, preliminary research and anecdotal reports suggest that Zinc-Thymulin holds significant potential in the field of hair follicle regeneration and restoration.
FAQ
Does zinc help the thymus?
Yes, zinc plays a crucial role in thymus function by supporting the production of thymic hormones, including thymulin, which is essential for immune regulation and T-cell maturation, as well as maintaining anagen.
What is thymulin used for?
Thymulin is primarily used for immune modulation, promoting T-cell differentiation, and reducing inflammation in the human body. It has potential therapeutic applications in autoimmune diseases, infections, dermatological conditions, and may help promote hair growth.
What type of zinc is best for hair growth?
Zinc picolinate and zinc methionine are considered the best forms for hair growth due to their high bioavailability and absorption. According to a medical journal hair therapy, these forms of zinc may support hair health more effectively.
What is the best peptide for hair loss?
Some of the most effective peptides for hair loss, including male pattern baldness, include Zinc-Thymulin, GHK-Cu (Copper Peptide), and PTD-DBM, as they promote hair follicle health, reduce inflammation, and support hair regrowth.
What does thymulin peptide do?
Thymulin peptide helps regulate immune function, reduces inflammation, and supports skin and hair follicle health by modulating cellular activity to regulate healthy hair growth and treat male pattern baldness
Does zinc reduce DHT levels in hair?
Yes, zinc has been shown to inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair loss. Additionally, zinc may help regulate hair growth by supporting overall scalp health and follicle function.
What is thymulin hormone?
Thymulin is a thymus-derived nonapeptide hormone that plays a key role in immune system regulation and T-cell differentiation, and hair loss involves inactivation of certain biological processes related to immune function, making it relevant to explore how thymulin may help regenerate hair lost.
What is the function of Thymuline?
Thymulin (also spelled Thymuline) enhances immune function by influencing T-cell activity and reducing inflammatory responses, which may also play a role in the phase of hair follicles and contribute to hair restoration methods.
What is the function of thymalin?
Thymalin is another thymic peptide that promotes immune system balance, supports T-cell function, and has anti-aging effects.
What is the function of the thymosin hormone?
Thymosin hormones, including thymosin alpha-1 and thymosin beta-4, play roles in immune system regulation, tissue repair, and cellular regeneration, alongside the action of naturally occurring copper complexes in supporting these processes
What are the effects of Thymulin?
Thymulin enhances immune function, reduces inflammation, supports skin and hair follicle health, induces differentiation, and may help prevent noticeable hair loss, as well as having neuroprotective properties.
Is zinc a good DHT blocker?
Yes, zinc can act as a mild DHT blocker by inhibiting 5-alpha reductase, which helps reduce hair loss associated with high DHT levels, particularly by affecting the fat scalp layer that plays a role in hair follicle health, especially in the western population.
What type of zinc is best for hair loss?
Zinc picolinate, zinc methionine, and zinc gluconate are commonly recommended for hair loss because hair loss occurs due to zinc deficiency, and these forms have superior absorption.
What is Zn-Thymulin?
Zn-Thymulin is a synthetic peptide combining zinc and thymulin, designed to support hair growth, reduce scalp inflammation, and enhance immune function. It has been studied for its potential benefits in conditions like androgenic alopecia.
Can zinc cause hair thinning?
Zinc deficiency can cause hair thinning, but excessive zinc intake may also lead to hair loss by disrupting the balance of other essential minerals like copper, which are crucial for the active growth phase. It is important to consider the established efficacy of maintaining a balanced intake of zinc and other minerals to support healthy hair growth.
Is zinc better than biotin for hair growth?
Both are important for hair health. Zinc supports follicle function and reduces DHT, while biotin aids in keratin production. Natural compounds involved can influence these processes. The best approach depends on the cause of hair loss.
Does zinc restore hair loss?
Zinc can help restore hair loss caused by zinc deficiency in the adult human population, but it may not be as effective for genetic or hormonal hair loss without additional treatments. Early reports suggest that zinc may help reduce scalp irritation, which can contribute to hair health.
Which is better for hair loss, biotin or zinc?
Both have different roles—biotin strengthens hair structure, while zinc supports follicle function and hormonal balance. A combination is often ideal for treated treatment.
Which type of zinc is best for hair growth?
Zinc picolinate, zinc methionine, and zinc gluconate are preferred for their superior absorption and bioavailability, with proven clinical results published supporting their effectiveness.
Can taking zinc regrow hair?
If hair loss is due to zinc deficiency, supplementing with zinc can support regrowth and help grow hair. However, it may not be sufficient for androgenetic alopecia on its own.
Does zinc really help with hair loss?
Yes, mineral zinc helps with hair loss by supporting follicle health, reducing DHT, and preventing deficiencies that contribute to shedding.
How does Thymulin work?
Thymulin works by regulating T-cell activity, modulating immune responses, and reducing inflammation, which benefits skin, hair follicles, and overall immune health while minimizing adverse systemic effects.
Does GHK-Cu regrow hair?
Yes, GHK-Cu (Copper Peptide) has been shown to stimulate hair growth, improve follicle health, and reduce inflammation, making it a popular choice for hair loss treatments, with some studies also exploring its potential in combination with stem cells for enhanced regenerative effects.
Does zinc stop hair thinning?
Zinc can help prevent hair thinning caused by nutritional deficiencies or excessive DHT levels, but it may not fully stop genetic hair loss or alter your hair color.
What does Thymulin peptide do?
Thymulin peptide, a nonapeptide hormone derived, supports immune function, reduces inflammation, and plays a role in skin and hair follicle health.
Does topical zinc block DHT?
Topical zinc has been suggested to inhibit 5-alpha reductase, which may help lower DHT levels on the scalp and reduce hair loss, as it is primarily produced in the hair follicles.
Can too much zinc cause hair thinning?
Yes, excessive zinc intake can disrupt the balance of other essential minerals like copper in the male population, leading to hair thinning and other health issues.
Reference
-
Meier N, Langan D, Hilbig H, et al. Thymic peptides differentially modulate human hair follicle growth. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(5):1516-9.
Thymic peptides differentially modulate human hair follicle growth. J Invest Dermatol
Thymus-derived protein extracts have been claimed to stimulate human hair growth, but there is no strong evidence supporting this. This study investigates whether human scalp hair follicles express thymic peptides (TYL, TB4, PTMA) and their potential effects on hair growth.
You can read the full article at
https://www.jidonline.org/article/S0022-202X(15)35747-X/fulltext.Coto JA, Hadden EM, Sauro M, Zorn N, Hadden JW. Interleukin 1 regulates secretion of zinc-thymulin by human thymic epithelial cells and its action on T-lymphocyte proliferation and nuclear protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89(16):7752-6.
Interleukin 1 regulates secretion of zinc-thymulin by human thymic epithelial cells and its action on T-lymphocyte proliferation and nuclear protein kinase C
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) stimulates zinc uptake by thymic epithelial cells (TEC), influencing thymulin secretion and T-lymphocyte maturation. IL-1 also induces metallothionein mRNA expression in TEC, facilitating zinc transfer to thymulin, which in turn activates nuclear protein kinase C in lymphocytes.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1502195/.Isakov N, Altman A. Regulation of immune system cell functions by protein kinase C. Front Immunol. 2013;4:384. Published 2013 Nov 18. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00384.
Regulation of immune system cell functions by protein kinase C. Front Immunol
Protein kinase C (PKC) enzymes are crucial regulators of immune cell functions, modulating signal transduction pathways that control T cell activation, proliferation, and polarization. This collection of studies explores the distinct roles of PKC isoforms, particularly PKCθ, in immune regulation, T cell signaling, and disease intervention, highlighting their potential as therapeutic targets in autoimmunity and transplantation.
You can read the full article at
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00384/fullLim PS, Sutton CR, Rao S. Protein kinase C in the immune system: from signalling to chromatin regulation. Immunology. 2015;146(4):508-22.
Protein kinase C in the immune system: from signalling to chromatin regulation
Protein kinase C (PKC) enzymes play a crucial role in signaling pathways by phosphorylating serine/threonine residues, regulating cellular functions like proliferation and gene expression. This review explores PKC’s role in immune cell signaling, its traditional cytoplasmic functions, and emerging evidence of its involvement in nuclear signal transduction and chromatin regulation.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26194700/.Haddad JJ. Thymulin and zinc (Zn2+)-mediated inhibition of endotoxin-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines and NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and activation in the alveolar epithelium: unraveling the molecular immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory effect of thymulin/Zn2+ in vitro. Mol Immunol. 2009;47(2-3):205-14.
ymulin and zinc (Zn2+)-mediated inhibition of endotoxin-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines and NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and activation in the alveolar epithelium: unraveling the molecular immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory effect of thymulin/Zn2+ in vitro.
Thymulin and zinc (Zn²⁺) exhibit anti-inflammatory effects in fetal alveolar type II epithelial cells by reducing IL-1β secretion, with thymulin acting via a cAMP-mediated, NF-κB-dependent pathway. Zn²⁺ independently suppresses IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 at high doses, and together, they synergistically modulate inflammatory responses.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19850345/.
Patient Success Stories

Before
After

At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health.
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer

Before
After

I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics. Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old Actress (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
Free Consultation
Start Your Journey to a Younger, Healthier You!
Categories
Information
Free Consultation
STEPS AWAY FROM A YOUNGER. HEALTHIER YOU!
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have








