Peptides
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
- Potential Health Benefits of Tesamorelin
- Key Takeaways
- What is Tesamorelin?
- How Tesamorelin Works
- Chemical Structure of Tesamorelin
- Research on Tesamorelin
- Associated Side Effects of Tesamorelin
- Tesamorelin vs Sermorelin
- Tesamorelin vs Sermorelin
- Tesamorelin vs Ipamorelin
- Tesamorelin Peptide Dosage
- FAQ
- References
Table of Contents
- Potential Health Benefits of Tesamorelin
- Key Takeaways
- What is Tesamorelin?
- How Tesamorelin Works
- Chemical Structure of Tesamorelin
- Research on Tesamorelin
- Associated Side Effects of Tesamorelin
- Tesamorelin vs Sermorelin
- Tesamorelin vs Sermorelin
- Tesamorelin vs Ipamorelin
- Tesamorelin Peptide Dosage
- FAQ
- References
Potential Health Benefits of Tesamorelin
- Promotes fat loss [1-9]
- Improves cognitive function [10-19]
- Improves lipid profile [1, 9, 20-23]
- Improves liver health [24-26]
- Lowers blood sugar levels [9, 27]
- Lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease [1, 21, 28]
- Treats nerve injury [29]
Key Takeaways
- Tesamorelin is a synthetic analog of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). It stimulates the pituitary gland to produce and release growth hormone, which in turn affects various metabolic processes, including fat metabolism.
- It is FDA-approved for the treatment of lipodystrophy in HIV-positive patients. This condition involves abnormal fat accumulation, particularly in the abdomen, and tesamorelin helps reduce visceral adipose tissue (VAT).
- Beyond reducing VAT, tesamorelin may improve lipid profiles and insulin sensitivity in patients with metabolic dysfunction, though its effects on these parameters may vary.
- Common side effects include joint pain, redness or irritation at the injection site, nausea, and headaches. It is contraindicated in patients with active malignancies or a history of hypersensitivity to GHRH.
- Research is exploring its potential in conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), age-related metabolic changes, and cognitive decline. However, its off-label use requires careful consideration due to limited long-term safety data.
What is Tesamorelin?
Tesamorelin is an FDA-approved drug for lipodystrophy, a medical condition characterized by an abnormal distribution of body fat. This small molecule (known as peptides) is a synthetic analog of growth hormone–releasing factor, which means that it stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete growth hormone (GH). This mechanism is thought to play an integral role in body fat reduction since direct GH administration has fat-burning effects.
How Tesamorelin Works
Tesamorelin stimulates the synthesis and release of GH by acting on the pituitary cells in the brain. The increase in GH also increases the levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1). This, in turn, stimulates muscle growth and fat loss. The promotion of muscle growth by Tesamorelin can be beneficial for individuals seeking to enhance their physical performance or improve their body composition. With consistent use and a proper exercise regimen, Tesamorelin can support significant muscle growth over time. However, it’s essential to note that tesamorelin, like any medication, may have unwanted effects, and individuals should discuss these potential side effects with their healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Chemical Structure of Tesamorelin
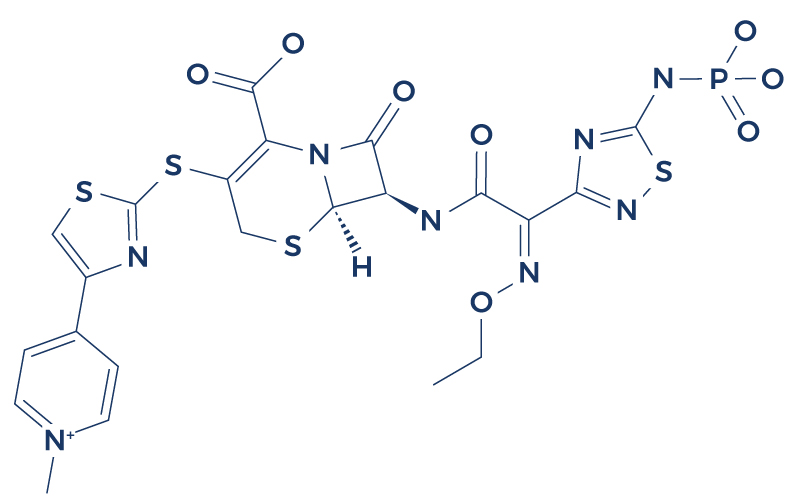
Research on Tesamorelin
A. Promotes Fat Loss

Fat reduction is the major benefit of tesamorelin. In fact, the US Food and Drug Administration approved tesamorelin last November 2010 for the reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy. Several lines of evidence clearly support this fat-burning effect:
- In HIV patients with central fat accumulation, subcutaneous injection of tesamorelin at a dose of 2 mg was generally well tolerated and resulted in a sustained decrease in visceral adipose tissue (the active component of total body fat).
- A 2010 study published in the Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes found that tesamorelin reduced visceral fat (body fat stored within the abdominal cavity) by approximately 18% and improved body image distress in HIV-infected patients with central fat accumulation.
- A 2011 study published in HIV/AIDS – Research and Palliative Care has shown that tesamorelin is safe and effective in reducing central fat accumulation among HIV-infected patients.
- In HIV patients with abdominal adiposity, tesamorelin reduced visceral adipose tissue by increasing adiponectin, a protein that breaks down fat.
- In patients with HIV-related lipodystrophy, 52 weeks of tesamorelin treatment reduced abdominal fat.
- A 2015 study published in PLoS One Journal found that patients with baseline metabolic syndrome, elevated triglyceride levels, or white race were most likely to experience reductions in visceral adipose tissue following 6 months of tesamorelin treatment.
- In HIV-infected patients with excess abdominal fat, treatment with tesamorelin reduced visceral adipose tissue and maintained the reduction for up to 52 weeks.
- In HIV-infected patients with abdominal fat accumulation, daily tesamorelin treatment for 26 weeks decreased visceral fat by 15.2% compared to placebo.
- In HIV-infected patients receiving tesamorelin, reduction in visceral adipose tissue was accompanied by improvement in metabolic profile.
B. Improves Cognitive Function

Growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH) such as tesamorelin has a potent effect on brain function. Studies show that this “cognitive enhancer” may benefit people with age-related memory problems and those suffering from chronic, progressive mental deterioration:
- In older adults with memory impairment, short-term tesamorelin administration improved executive function and verbal memory. [10]
- Daily subcutaneous injections of tesamorelin for 20 weeks improved executive function, verbal memory, and visual memory in both adults with mild cognitive impairment and healthy older adults. [11]
- In patients with mild cognitive impairment, tesamorelin administration at a dose of 1mg/day for 10 weeks improved various areas of cognition. [12]
- A 2012 study published in Nature Reviews Endocrinology found that tesamorelin administration in patients with age-related cognitive impairment significantly improved memory and thinking skills. [13]
- In adults with mild cognitive impairment, daily subcutaneous injections of tesamorelin increased GH levels and improved executive function and verbal memory. [14-15]
- In normal older adults and adults with mild cognitive impairment, tesamorelin administration for 5 months demonstrated favorable effects on cognition. [16]
- Self-administration of tesamorelin at 1 mg 30 minutes before bedtime slowed cognitive decline in older adults. [17]
- An ongoing Phase II trial of tesamorelin for cognition in aging HIV-infected persons shows promising results with the tesamorelin-treated group exhibiting improvement in neurocognitive performance. [18]
- In adults with mild cognitive impairment, administration of daily subcutaneous injections of tesamorelin significantly increased the levels of gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that facilitates brain cell communication. [19]
C. Improves Lipid Profiles

The ability of tesamorelin to improve lipid profile can be attributed to its fat-burning effect and GH-boosting properties. High-quality studies support its beneficial effect on triglycerides, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (bad cholesterol), and high-density lipoprotein (good cholesterol):
- In HIV patients with abdominal fat accumulation, subcutaneous injection of tesamorelin at a dose of 2 mg significantly improved triglycerides and total cholesterol levels. [1]
- The administration of tesamorelin in HIV-infected patients resulted in a greater reduction in triglycerides compared to placebo treatment. [9]
- Treatment of type 2 diabetic patients with tesamorelin for 12 weeks significantly reduced total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein. [20]
- In HIV-infected patients with excess abdominal fat, tesamorelin treatment increased the levels of high-density lipoprotein. [21]
- In patients with HIV, a daily subcutaneous injection of tesamorelin resulted in decreased visceral fat and improved lipid profiles. [22-23]
D. Improves Liver Health

Studies also show that tesamorelin may benefit liver function through various important mechanisms:
- In HIV-infected men and women with hepatic steatosis (accumulation of fat in the liver), treatment with tesamorelin for 12 months significantly reduced liver fat. [24]
- In HIV-infected patients with abdominal obesity who received tesamorelin, a clinically significant reduction in body fat was associated with improved liver enzymes. [25]
- In obese subjects with reduced GH, 12 months of tesamorelin treatment led to a significantly greater increase in phosphocreatine, a substance that protects the liver from low levels of oxygen and impaired blood flow. [26]
E. Lowers Blood Sugar Levels

Clinical trials also show that tesamorelin can bring down high blood sugar levels by promoting fat loss:
- The administration of tesamorelin in HIV-infected patients did not only promote abdominal fat loss but also reduced blood sugar levels after 52 weeks of treatment. [9]
- Tesamorelin treatment for 26 weeks also reduced blood sugar levels in HIV-infected patients with excess abdominal fat. [27]
Tesamorelin, classified as a synthetic GHRH, demonstrates promising effects beyond fat reduction, including the potential to improve metabolic parameters like blood sugar levels.
Tesamorelin, as a synthetic GHRH, exhibits multifaceted benefits beyond fat reduction, including the potential to improve metabolic parameters like blood sugar levels.
F. Lowers the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Evidence suggests that tesamorelin can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by improving various health parameters such as triglyceride levels and total cholesterol levels. [1] Tesamorelin also has the ability to raise the levels of high-density lipoprotein (good cholesterol). [21] An increase in HDL cholesterol is associated with significant cardiovascular disease risk reduction. [28] These effects indicate that tesamorelin may contribute to a lower risk of cardiovascular events and promote overall heart health.
G. Treats Nerve Injury
Nerve injury is one of the most debilitating medical conditions and perhaps one of the most difficult to treat as it can lead to permanent impairment in motor and sensory function of the affected area. Research, however, suggests that growth hormone-based therapies such as tesamorelin treatment can speed up the rate of healing of damaged nerves. [29]
Associated Side Effects of Tesamorelin
Tesamorelin side effects are very uncommon. There have been some side effects associated with the use of this drug wherein the patient had one of the issues listed below at some point while being on tesamorelin. However, these side effects weren’t confirmed to be associated with the treatment and could have been a coincidence and not related to the use of tesamorelin. Despite this, it was listed as a side effect associated with tesamorelin even though these associated side effects are very uncommon.
Side effects associated with tesamorelin may include the following:
- Difficulty breathing
- Dizziness
- Elevations in blood sugar levels
- Fast heartbeat
- Hives
- Irritation or itching
- Joint pain
- Night sweats
- Numbness
- Rash
- Swelling of the face and throat
- Vomiting
Tesamorelin Tablets
Tesamorelin tablets represent a significant advancement in the field of peptide therapy, offering a convenient and effective way to administer this synthetic peptide. Developed to mimic the effects of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), Tesamorelin tablets stimulate the pituitary gland to produce and release growth hormone (GH). This mechanism of action makes them particularly promising in addressing conditions characterized by growth hormone deficiency or dysregulation, such as HIV-associated lipodystrophy.
One of the key advantages of Tesamorelin tablets is their ease of use and portability, providing patients with a convenient method of receiving treatment. Unlike traditional injectable forms of peptide therapy, which may require frequent administration and careful handling, Tesamorelin tablets offer a more user-friendly option. This can improve patient adherence to treatment regimens and enhance overall treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, Tesamorelin tablets have shown promising results in clinical studies for reducing excess abdominal fat, a common concern in individuals with HIV-associated lipodystrophy. By targeting visceral adipose tissue, Tesamorelin tablets have the potential to improve body composition and metabolic health in this patient population. Overall, Tesamorelin tablets represent a valuable therapeutic option for individuals seeking to address growth hormone deficiency and related conditions in a convenient and effective manner.
Tesamorelin vs Sermorelin
Tesamorelin and Sermorelin are both synthetic peptides designed to stimulate the release of growth hormone (GH) by mimicking the effects of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). While they share a common mechanism of action, there are key differences between the two peptides that may influence their suitability for different therapeutic applications. Tesamorelin is specifically indicated for the treatment of excess abdominal fat in individuals with HIV-associated lipodystrophy, whereas Sermorelin is often used more broadly for the management of growth hormone deficiency and related conditions. Tesamorelin has been shown to increase adiponectin concentrations, a protein associated with improved metabolic health, although the effects of Sermorelin on adiponectin levels are less well-documented.
One significant difference between Tesamorelin and Sermorelin is their respective formulations and routes of administration. Tesamorelin is available in tablet form, providing a convenient and easily administered option for patients. In contrast, Sermorelin is typically administered via subcutaneous injection, which may be less convenient for some individuals. The differences in formulation and administration route may impact patient preference and adherence to treatment. While Tesamorelin tablets offer a user-friendly option, the inconvenience of subcutaneous injections with Sermorelin may lead to reduced compliance, potentially resulting in poorer treatment outcomes and obvious cardiometabolic consequences.
Another consideration when comparing Tesamorelin and Sermorelin is their safety and efficacy profiles. While both peptides have demonstrated effectiveness in stimulating GH release, they may vary in terms of side effects and tolerability. Clinical studies have shown that Tesamorelin is generally well-tolerated, with the most common side effects being mild and transient. Sermorelin has also been shown to have a favorable safety profile, but individual responses may vary. Ultimately, the choice between Tesamorelin and Sermorelin will depend on factors such as the specific indication for treatment, patient preferences, and individual response to therapy. The pulsatile release of growth hormone induced by these peptides may also influence their safety and efficacy profiles, as variations in GH levels could impact physiological processes and contribute to different side effect profiles.
Tesamorelin vs Ipamorelin
Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin are both synthetic peptides with similar but distinct mechanisms of action in stimulating the release of growth hormone (GH). Tesamorelin specifically mimics the action of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) by activating the GHRH receptor, leading to increased GH secretion from the pituitary gland. In contrast, Ipamorelin acts as a selective ghrelin receptor agonist, indirectly stimulating GH release by activating the ghrelin receptor. While both peptides ultimately result in elevated GH levels, their pathways of action differ, which may influence their clinical applications and side effect profiles.
One key difference between Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin is their selectivity for specific receptors in the body. Tesamorelin targets the GHRH receptor, which is primarily involved in regulating GH release, while Ipamorelin targets the ghrelin receptor, which plays a role in appetite regulation and energy balance in addition to GH secretion. As a result, Tesamorelin may have a more targeted effect on GH secretion, whereas Ipamorelin’s action on the ghrelin receptor may lead to additional effects on appetite and metabolism.
Another consideration when comparing Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin is their respective safety and tolerability profiles. Clinical studies have demonstrated that both peptides are generally well-tolerated, with few adverse effects reported. However, individual responses to treatment may vary, and side effects such as injection site reactions, headache, and gastrointestinal symptoms have been reported with both Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin. Ultimately, the choice between Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin will depend on factors such as the specific indication for treatment, patient preferences, and individual response to therapy.
Tesamorelin Peptide Dosage
Tesamorelin peptide dosage typically varies depending on the specific medical condition being treated and individual patient factors. For the management of excess abdominal fat in individuals with HIV-associated lipodystrophy, the recommended dosage of Tesamorelin is typically 2 mg administered once daily via subcutaneous injection. It’s important for patients to follow the dosage instructions provided by their healthcare provider to ensure optimal treatment outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
The dosage of Tesamorelin may be adjusted based on factors such as the patient’s response to treatment, overall health status, and any underlying medical conditions. Healthcare providers may monitor patients regularly during treatment to assess the effectiveness of Tesamorelin therapy and make any necessary dosage adjustments as needed. Additionally, patients should not exceed the prescribed dosage of Tesamorelin or alter their treatment regimen without consulting their healthcare provider.
As with any medication, it’s crucial for patients to adhere to the prescribed Tesamorelin dosage and administration schedule to achieve the desired therapeutic effects. Patients should also report any potential side effects or concerns to their healthcare provider promptly. By following the recommended dosage and guidance from their healthcare provider, patients can optimize the benefits of Tesamorelin therapy while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. This adherence helps maintain a consistent blood level of the medication, ensuring its efficacy in targeting visceral fat and enhancing muscle tone.
FAQ
What is tesamorelin used for?
Tesamorelin is used primarily to reduce excess abdominal fat in HIV patients with lipodystrophy. It is also being investigated for its potential benefits in non-HIV individuals with similar fat accumulation issues. Studies utilizing computed tomography have shown promising results in assessing the efficacy of tesamorelin in reducing visceral adipose tissue, providing objective measurements of fat loss in clinical trials. This imaging technique allows for precise quantification of adipose tissue distribution, enabling researchers to evaluate the effectiveness of tesamorelin in targeting specific fat deposits. By employing computed tomography scans, researchers can track changes in visceral fat volume over time, providing valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of tesamorelin for improving metabolic health.
What does tesamorelin do for bodybuilding?
In bodybuilding, tesamorelin is used to enhance body composition by reducing abdominal fat and potentially increasing lean muscle mass, making it popular for improving physique. This is particularly beneficial for bodybuilders aiming to achieve a more defined and sculpted appearance, as excess fat can obscure muscle definition. Additionally, tesamorelin may help reduce the appearance of lipid-engorged adipocytes, further contributing to a leaner and more toned physique.
Is tesamorelin peptide legal?
Tesamorelin is legal in the United States for prescribed medical use, specifically for the treatment of HIV-related lipodystrophy. Its use outside prescribed guidelines, such as in bodybuilding, may not be legal. While tesamorelin has shown effectiveness in reducing excess abdominal fat in HIV patients, its safety and efficacy in the general population, especially for purposes like bodybuilding, have not been thoroughly studied or approved. Therefore, using tesamorelin for non-medical reasons may pose legal risks and health concerns for individuals outside the prescribed medical context.
Does tesamorelin actually work?
Tesamorelin has been clinically proven to reduce visceral abdominal fat in patients with HIV-associated lipodystrophy. Its effectiveness for other uses has not been as extensively validated. While it may offer potential benefits for improving body composition and addressing certain health concerns, such as metabolic abnormalities, its impact on muscle mass and lower density in non-HIV individuals requires further research and validation.
What does Tesamorelin peptide do?
Tesamorelin stimulates the body’s release of growth hormone, which leads to reduced visceral fat and improved body composition, including lower VAT.
Is Tesamorelin peptide legal?
Yes, tesamorelin is legal for use with a prescription in the United States, primarily for treating HIV-related excess abdominal fat. Tesamorelin and Sermorelin are both synthetic two peptides designed to stimulate the release of growth hormone (GH) by mimicking the effects of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH).
What is Tesamorelin used for in bodybuilding?
In bodybuilding, tesamorelin is used to decrease body fat, particularly abdominal fat, and to improve overall body composition. While tesamorelin is a popular choice for reducing fat, other peptides like CJC-1295 are also used in bodybuilding to enhance muscle growth and recovery.
How effective is Tesamorelin?
Tesamorelin plays a significant role in reducing abdominal fat in HIV-infected individuals with lipodystrophy, with many patients seeing significant results within a few months. Its effectiveness in addressing aging-related changes in body composition is also being studied, suggesting a potential role in combating certain aspects of the aging process. Studies indicate that tesamorelin may not only improve body composition but also enhance metabolic homeostasis, potentially slowing down the aging process and promoting overall health and well-being.
How long does it take for Tesamorelin to work?
The effects of tesamorelin on reducing abdominal fat can be seen as early as 2 to 3 months after the commencement of daily injections. This rapid response suggests a favorable impact on metabolic health and may contribute to reducing the risk of conditions associated with excess abdominal fat, such as inflammatory organ like the liver.
Does Tesamorelin actually work?
Yes, tesamorelin effectively reduces excess abdominal fat in individuals with HIV-associated lipodystrophy, as supported by clinical trials.
Does Tesamorelin need to be cycled?
Yes, it is often recommended to cycle tesamorelin, as continuous long-term use may lead to diminished effects due to possible antibody formation.
Does Tesamorelin increase muscle mass?
While tesamorelin primarily targets fat reduction, it may indirectly support muscle growth through its role in stimulating growth hormone release. Growth hormone plays a crucial role in regulating various metabolic processes, including protein synthesis and tissue repair, which are essential for muscle growth. Therefore, by promoting the secretion of growth hormone, tesamorelin can contribute to the enhancement of muscle mass and strength. However, its direct effects on immune cells may not be significant, as its primary function is related to metabolic regulation rather than immune system modulation.
Is it safe to take tesamorelin?
Ipamorelin works well for stimulating growth hormone release, but like any medication, it’s essential to use it under medical supervision to minimize potential risks and side effects.
What are the benefits of tesamorelin?
The primary benefits of tesamorelin include significant reduction of visceral abdominal fat and improvement in body composition in patients with lipodystrophy. This reduction in fat is not just in terms of quantity but also in terms of quality, as tesamorelin has been shown to target poorer quality adipocytes, leading to a more favorable metabolic profile.
How long does it take for tesamorelin to work?
Results from tesamorelin, particularly in the reduction of abdominal fat, can typically be observed within two to three months of starting treatment. This timeframe may vary depending on individual response to the therapy and other factors such as diet and exercise. However, tesamorelin has been shown to have a significant impact on metabolic homeostasis, promoting a more balanced state within the body’s metabolic processes. By targeting visceral adipose tissue and improving fat quality, tesamorelin helps restore metabolic balance, contributing to overall health improvements.
Does tesamorelin cause weight loss?
Tesamorelin causes fat loss, particularly in the abdominal area, which may contribute to overall weight loss in some individuals. This reduction in abdominal fat can lead to improvements in body composition and metabolic health. Additionally, tesamorelin has been shown to improve fat quality by reducing visceral adipose tissue, which is associated with a higher risk of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. By targeting visceral fat, tesamorelin helps to improve fat quality and promote better metabolic function. Overall, the fat loss induced by tesamorelin can have significant benefits for individuals seeking to improve their overall health and well-being.
How does tesamorelin make you feel?
Users of tesamorelin may feel an improvement in their overall energy levels and physical appearance, but side effects like joint and muscle pain can occur. These side effects are often temporary and resolve with continued use of the medication. However, it’s essential to be aware of potential adverse effects and to consult with a healthcare provider if any concerns arise. In some cases, joint and muscle pain may be due to changes in connective tissue structure or function, which can occur as a result of tesamorelin treatment. It’s important to monitor for any changes in symptoms and to discuss them with a healthcare professional for appropriate management.
Where can I buy tesamorelin?
Tesamorelin can be purchased through pharmacies with a valid prescription from a healthcare provider, specifically for treating lipodystrophy in HIV patients. Additionally, while its primary indication is for addressing excess abdominal fat, Tesamorelin may also have ancillary benefits such as improving bone density in individuals with HIV-associated lipodystrophy.
What is Tesamorelin good for?
Tesamorelin is effective for reducing excess abdominal fat in HIV patients with lipodystrophy and improving related metabolic parameters. Additionally, it may have potential benefits for bone density in this population, although further research is needed to fully understand its effects on skeletal health. Overall, Tesamorelin represents a promising therapeutic option for addressing both the aesthetic and metabolic concerns associated with HIV-associated lipodystrophy.
How long does it take to see results from Tesamorelin?
Results, particularly in terms of reduced abdominal fat, can typically be seen within 2 to 3 months of consistent use. This timeframe may vary depending on individual response to the treatment and other factors such as diet and exercise. However, tesamorelin has been shown to have a significant impact on body composition and metabolism, which can contribute to a slower aging process and improved overall health.Results, particularly in terms of reduced abdominal fat, can typically be seen within 2 to 3 months of consistent use. This timeframe may vary depending on individual response to the treatment and other factors such as diet and exercise. However, tesamorelin has been shown to have a significant impact on body composition and metabolism, which can contribute to a slower aging process and improved overall health. Consistent use of tesamorelin over time may also help in mitigating some of the effects of aging, such as loss of muscle mass and increased body fat accumulation.
How often should I take Tesamorelin?
Tesamorelin is usually administered once daily as a subcutaneous injection under medical guidance. It stimulates the pituitary gland to produce and release growth hormone, which in turn increases the levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) in the body, leading to various metabolic effects such as reduced body fat and improved muscle mass.
Does Tesamorelin cause weight loss?
Yes, tesamorelin can lead to weight loss primarily through the reduction of abdominal fat. This reduction in fat quantity has been demonstrated in various clinical studies, showing significant decreases in visceral adipose tissue among individuals with conditions such as HIV-associated lipodystrophy. Additionally, tesamorelin’s ability to target specific areas of fat accumulation, particularly in the abdominal region, makes it an effective option for those seeking to improve their body composition and metabolic health. Overall, tesamorelin’s impact on fat quantity underscores its potential as a therapeutic intervention for addressing excess fat accumulation in certain patient populations.
What is the best peptide for fat loss?
While several peptides are known for promoting fat loss, tesamorelin is particularly noted for its effectiveness in reducing visceral fat. However, it’s essential to note that tesamorelin’s benefits extend beyond fat reduction, as it has also been shown to promote enhanced muscle growth. This dual action of tesamorelin makes it a valuable tool in improving body composition and overall metabolic health. Additionally, the ability of tesamorelin to target visceral fat while simultaneously supporting enhanced muscle growth highlights its potential as a comprehensive approach to optimizing physical fitness and well-being.
How does Tesamorelin make you feel?
Tesamorelin can increase feelings of well-being due to improvements in body composition, though some may experience discomfort from side effects. These side effects can include injection site reactions, joint pain, or changes in glucose tolerance. However, these effects are usually mild and temporary. Overall, the reduction in subcutaneous fat and improvement in body composition provided by tesamorelin can contribute to an enhanced sense of physical and emotional wellness.
Is Tesamorelin better than Ipamorelin?
Tesamorelin is specifically effective for reducing abdominal fat, making it better for specific therapeutic needs associated with metabolically healthy obesity compared to Ipamorelin, which is generally used for broader growth hormone release stimulation.
Should I take sermorelin or Ipamorelin?
Choosing between sermorelin and Ipamorelin depends on individual goals; sermorelin stimulates a more pronounced increase in growth hormone, while Ipamorelin provides a more gradual and sustained release, affecting hormonal and neuronal signals differently.
Is CJC-1295 better than sermorelin?
CJC-1295, classified among growth hormone secretagogues, tends to provide longer-lasting effects in growth hormone release compared to sermorelin, making it potentially better for those seeking longer-term benefits.
Can you take Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin together?
Combining tesamorelin and Ipamorelin may be beneficial for enhancing overall growth hormone levels and improving body composition, but should only be done under medical supervision. While tesamorelin primarily targets reducing excess abdominal fat, Ipamorelin is known for its ability to promote muscle growth. Together, they can offer a synergistic effect, potentially leading to enhanced muscle growth and fat loss. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure proper dosing and monitoring for optimal results and safety. When used appropriately, this combination therapy may support individuals seeking to improve their physique and overall health.
What is better than Ipamorelin?
The effectiveness of peptides like Ipamorelin can depend on specific goals; tesamorelin might be superior for targeted fat reduction, while others like CJC-1295 could be better for sustained growth hormone levels. Ipamorelin has shown promise in promoting the release of growth hormone, which can have various effects on metabolism, including increased fat metabolism and reduction of subcutaneous adipose tissue. This targeted action on subcutaneous adipose tissue makes Ipamorelin a potential option for individuals seeking to address localized fat deposits and improve body composition.
What are the benefits of Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin?
Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin both offer significant benefits in stimulating growth hormone, which can lead to reduced body fat, improved muscle mass, and better overall metabolic health. For individuals with growth hormone deficiency, these peptides can be particularly valuable in restoring hormone levels to normal ranges, thereby addressing symptoms associated with this condition such as decreased muscle strength, increased body fat, and reduced bone density. By promoting the production and release of growth hormone, Tesamorelin and Ipamorelin offer a targeted approach to managing growth hormone deficiency and improving overall health and well-being.
Is sermorelin the same as Ipamorelin?
Sermorelin and Ipamorelin are not the same; sermorelin directly stimulates the pituitary to release growth hormone, whereas Ipamorelin acts more selectively, minimizing potential side effects. Both are classified as growth hormone releasing peptides, but their mechanisms of action differ. While sermorelin triggers the release of growth hormone by mimicking the action of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), Ipamorelin stimulates the pituitary gland to produce growth hormone in a pulsatile manner, offering a more targeted approach to hormone stimulation.
Reference
Falutz J, Allas S, Mamputu JC, et al. Long-term safety and effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue, in HIV patients with abdominal fat accumulation. AIDS. 2008;22(14):1719-28.
Long-term safety and effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue, in HIV patients with abdominal fat accumulation
The objective of this study was to assess the long-term safety and effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue, in HIV patients with central fat accumulation. Patients initially randomized to tesamorelin or placebo for 26 weeks were rerandomized for another 26 weeks. Tesamorelin was generally well tolerated, with adverse events comparable to the initial phase. Glucose parameters remained stable, and VAT reduction (-18%) and triglyceride decrease (-51 mg/dl) were sustained over 52 weeks without worsening glucose levels. However, upon discontinuation, VAT reaccumulated, suggesting that the effects of tesamorelin on VAT are not long-lasting beyond treatment duration.
You can read the full article at https://journals.lww.com/aidsonline/fulltext/2008/09120/long_term_safety_and_effects_of_tesamorelin,_a.6.aspx.
Falutz J, Potvin D, Mamputu JC, et al. Effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor, in HIV-infected patients with abdominal fat accumulation: a randomized placebo-controlled trial with a safety extension. J Acquir Immune DeficSyndr. 2010;53(3):311-22.
Effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor, in HIV-infected patients with abdominal fat accumulation: a randomized placebo-controlled trial with a safety extension
In this 12-month study of HIV-infected patients with excess visceral fat, tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor, significantly reduced visceral adipose tissue (VAT) by approximately 10.9% compared to placebo in the first 6-month phase, with further reduction over 12 months. Secondary measures including trunk fat, waist circumference, and waist-hip-ratio also improved. Insulin-like growth factor-1 increased without adverse effects on glucose. Patient and physician assessments showed improved body image distress. Tesamorelin was well tolerated, but VAT reductions were rapidly reversed upon discontinuation. Overall, tesamorelin demonstrated sustained efficacy in reducing VAT and improving body image distress in HIV patients without significant adverse effects.
You can read the full article at https://journals.lww.com/jaids/fulltext/2010/03010/effects_of_tesamorelin,_a_growth_hormone_releasing.5.aspx.
Bedimo R. Growth hormone and tesamorelin in the management of HIV-associated lipodystrophy. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2011;3:69–79. doi:10.2147/HIV.S14561.
Growth hormone and tesamorelin in the management of HIV-associated lipodystrophy
HIV-infected patients undergoing highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) often experience body composition changes, including peripheral fat loss and central fat accumulation, which can lead to significant distress and affect treatment adherence. Current treatment options have limitations and potential complications. Tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing hormone analog, has been developed to address central fat accumulation in HIV patients. Clinical trials have demonstrated its safety and effectiveness in reducing central fat accumulation, although its long-term cardiovascular benefits remain uncertain, and the effect is temporary.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3218714/.
Stanley TL, Falutz J, Mamputu JC, Soulban G, Potvin D, Grinspoon SK. Effects of tesamorelin on inflammatory markers in HIV patients with excess abdominal fat: relationship with visceral adipose reduction. AIDS. 2011;25(10):1281-8.
Effects of tesamorelin on inflammatory markers in HIV patients with excess abdominal fat: relationship with visceral adipose reduction
The study aimed to examine the impact of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing hormone analog, on inflammatory and fibrinolytic markers and their correlation with visceral adipose tissue (VAT) changes. Four hundred and ten HIV-infected patients with abdominal adiposity were randomized to receive 2 mg tesamorelin or placebo subcutaneously daily for 26 weeks. Results showed that tesamorelin treatment led to a significant decrease in tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) antigen levels compared to placebo. Changes in inflammatory markers correlated with changes in VAT among tesamorelin recipients, suggesting a potential modest beneficial effect on adiponectin and fibrinolytic markers. Further investigations are warranted to ascertain the clinical implications of these findings and underscore the importance of addressing excessive VAT in HIV patients.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3673013/.
Available from http://i-base.info/htb/2092.
Tesamorelin (TH9507) reduces abdominal fat in patients with HIV-related lipodystrophy: 52 week results
Results presented at the Retrovirus conference in February revealed a notable reduction in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) of approximately 20% among patients treated with growth hormone-releasing factor (GHRF) over 26 weeks, without adverse effects on limb fat. This improvement was accompanied by favorable lipid profile changes, including decreases in triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and TC:HDL ratio, along with an increase in HDL. In the extended study, patients initially assigned to GHRF were re-randomized to either continue GHRF (TT) or switch to placebo (TP), while those initially receiving placebo were switched to GHRF (PT). At week 52, patients continuing on GHRF (TT) maintained benefits observed at week 26, while those switching to placebo (TP) experienced a loss of benefits, returning close to baseline. Safety data showed no significant differences compared to placebo. Baseline characteristics were similar across groups, with notable reductions in VAT and waist circumference observed with GHRF treatment (p < 0.001).
You can read the abstract of the article at http://i-base.info/htb/2092.
Mangili A, Falutz J, Mamputu JC, Stepanians M, Hayward B. Predictors of Treatment Response to Tesamorelin, a Growth Hormone-Releasing Factor Analog, in HIV-Infected Patients with Excess Abdominal Fat. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0140358. Published 2015 Oct 12. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0140358.
Predictors of Treatment Response to Tesamorelin, a Growth Hormone-Releasing Factor Analog, in HIV-Infected Patients with Excess Abdominal Fat
In HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy, tesamorelin effectively reduces visceral adipose tissue (VAT). This study aimed to assess patient characteristics and disease-risk scores as predictors of VAT reduction during tesamorelin therapy and to explore factors associated with achieving VAT <140 cm2, a level linked with lower health risks. Analysis of two Phase 3 trials revealed that metabolic syndrome (MetS-IDF or MetS-NCEP) and Framingham Risk Score (FRS) were associated with baseline VAT. Metabolic syndrome (MetS-NCEP), elevated triglyceride levels, and white race were significant predictors of VAT reduction after 6 months of tesamorelin therapy. Odds of achieving VAT <140 cm2 with tesamorelin were 3.9 times higher compared to placebo. No predictive factors were identified at 3 months. These findings underscore the potential of tesamorelin in reducing VAT and highlight specific patient groups that may benefit most from therapy.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4601733/.
Falutz J, Mamputu JC, Potvin D, et al. Effects of tesamorelin (TH9507), a growth hormone-releasing factor analog, in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients with excess abdominal fat: a pooled analysis of two multicenter, double-blind placebo-controlled phase 3 trials with safety extension data. J ClinEndocrinolMetab. 2010;95(9):4291-304.
Effects of tesamorelin (TH9507), a growth hormone-releasing factor analog, in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients with excess abdominal fat: a pooled analysis of two multicenter, double-blind placebo-controlled phase 3 trials with safety extension data
In ART-treated HIV patients with excess abdominal fat, tesamorelin significantly reduces visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and maintains this reduction for up to 52 weeks, as evidenced by a pooled analysis of two phase-3 studies. At week 26, tesamorelin-treated patients experienced a notable decrease in VAT and improvements in lipid profiles compared to placebo. Additionally, tesamorelin improved body image perception without adversely affecting glucose parameters. These findings underscore the potential of tesamorelin as a therapeutic option for managing excess VAT in ART-treated HIV patients.
You can read the full article at https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/95/9/4291/2835394?login=false.
Falutz J, Allas S, Blot K, et al. Metabolic effects of a growth hormone-releasing factor in patients with HIV. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(23):2359-70.
Metabolic effects of a growth hormone-releasing factor in patients with HIV
In HIV-infected patients experiencing treatment-related accumulation of visceral adipose tissue, a 26-week treatment with the growth hormone-releasing factor analogue, tesamorelin, resulted in a significant reduction in visceral adiposity, accompanied by improvements in lipid profiles and insulin-like growth factor I levels compared to placebo. These findings suggest a potential therapeutic benefit of tesamorelin in managing central fat accumulation in HIV-infected individuals without significant adverse effects on glycemic measures.
You can read the full article at https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa072375?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
Stanley TL, Falutz J, Marsolais C, Morin J, Soulban G, Mamputu JC, et al. Reduction in visceral adiposity is associated with an improved metabolic profile in HIV-infected patients receiving tesamorelin. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:1642–1651.
Reduction in visceral adiposity is associated with an improved metabolic profile in HIV-infected patients receiving tesamorelin
In individuals with HIV-associated abdominal fat accumulation, treatment with tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing hormone analogue, resulted in a reduction of visceral adipose tissue (VAT) by 15%-20% over 6-12 months. In a per-protocol analysis of patients initially assigned to receive tesamorelin, those showing a ≥8% reduction in VAT demonstrated significantly greater improvements in triglyceride levels, adiponectin levels, and glucose homeostasis compared to nonresponders. These findings suggest that VAT reduction with tesamorelin is associated with favorable metabolic changes, highlighting its potential clinical significance in managing HIV-associated abdominal adiposity.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3348954/.
Available from https://www.alzheimersanddementia.com/article/S1552-5260(11)01582-2/abstract.
Baker LD, Barsness SM, Borson S, et al. Effects of growth hormone–releasing hormone on cognitive function in adults with mild cognitive impairment and healthy older adults: results of a controlled trial. Arch Neurol. 2012;69(11):1420-9.
Effects of growth hormone–releasing hormone on cognitive function in adults with mild cognitive impairment and healthy older adults: results of a controlled trial
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted at the University of Washington School of Medicine, 152 adults aged 55 to 87, including 66 with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), self-administered daily subcutaneous injections of tesamorelin (1 mg/d), a stabilized analog of human growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), or placebo for 20 weeks. Cognitive function was assessed using a battery of tests, with primary outcomes focusing on executive function, verbal memory, and visual memory. Results indicated a favorable effect of GHRH on cognition, particularly in executive function, with increased insulin-like growth factor 1 levels and reduced body fat observed. Adverse events were mild, suggesting the potential therapeutic benefit of GHRH administration for brain health in both healthy older adults and those with MCI. Further research is warranted to explore its long-term effects.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3764914/.
Available from https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02553603.
Mclarnon A. Neuroendocrinology: Tesamorelin can improve cognitive function. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8(10):568.
Neuroendocrinology: Tesamorelin can improve cognitive function
A recent study published in Archives of Neurology reveals that administering tesamorelin, a long-acting analogue of somatoliberin (growth-hormone-releasing hormone), to individuals with mild cognitive impairment or healthy older adults has shown positive effects on cognition. Lead investigator Laura Baker from the University of Washington explains that the study aimed to evaluate the impact of somatoliberin on executive function and short-term memory, particularly in those at risk of Alzheimer’s disease. The study involved 152 adults aged 55–87 years, with 137 completing the trial. Participants self-administered 1 mg of tesamorelin daily for 20 weeks, leading to sustained increases in insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) levels comparable to those of young adults. Cognitive tests assessing executive function and short-term memory were conducted at various intervals throughout the study, demonstrating promising results in cognition enhancement.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.nature.com/articles/nrendo.2012.151.
-
Growth hormone-releasing hormone had positive effect on cognition
A study led by Laura D. Baker, PhD, from the University of Washington School of Medicine, revealed that treatment with growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) had positive cognitive effects among adults with mild cognitive impairment and healthy older adults. The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involved 152 adults, with 66 having mild cognitive impairment, aged 55 to 87 years. Participants self-administered daily subcutaneous injections of tesamorelin (Egrifta, Theratechnologies) or placebo for 20 weeks. The study showed that GHRH significantly improved cognition, particularly in executive function and verbal memory, with notable increases in insulin-like growth factor 1 levels and reductions in body fat. Adverse events were mild, with 68% of GHRH-treated participants reporting them. The findings suggest the potential of GHRH administration in preserving or enhancing cognitive function in aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://www.healio.com/news/psychiatry/20120810/growth-hormone-releasing-hormone-had-positive-effect-on-cognition.
Vitiello MV, Moe KE, Merriam GR, Mazzoni G, Buchner DH, Schwartz RS. Growth hormone releasing hormone improves the cognition of healthy older adults. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:318-323.
Growth hormone releasing hormone improves the cognition of healthy older adults
The study investigated the impact of 6 months of daily treatment with growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) or placebo on the cognitive function of 89 healthy older adults with an average age of 68.0±0.7 years. Results showed that GHRH treatment led to significant improvements in various cognitive tasks, including WAIS-R performance IQ, picture arrangement, finding A’s, verbal sets, and single-dual task, with statistical significance (p<0.01 for all). These improvements were consistent across gender, estrogen status, and baseline cognitive capacity. The findings suggest that age-related cognitive decline may be linked to declines in the somatotrophic axis and that supplementation of this axis could mitigate cognitive decline in healthy older adults and potentially in those with impaired cognitive function like mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease.
You can read the full article at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0197458005000631?via%3Dihub.
Baker LD, Vitiello MV. Growth hormone-releasing hormone improves cognitive function in older adults: sleep on it–reply. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70(4):529-30.
Baker, L. D. et al. Effects of growthhormone-releasing hormone on cognitive function in adultswith mild cognitive impairment on healthy older adults.Arch. Neurol. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2012.1970.
Effects of growthhormone-releasing hormone on cognitive function in adultswith mild cognitive impairment on healthy older adults
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted at the Clinical Research Center of the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, 152 adults (66 with mild cognitive impairment [MCI]) aged 55 to 87 years participated. They self-administered daily subcutaneous injections of tesamorelin (1 mg/d) or placebo for 20 weeks, with blood samples collected at various intervals. Cognitive function was assessed using various tests, and results showed a significant positive effect of tesamorelin on cognition (P = .03), particularly in executive function (P = .005). Tesamorelin also increased insulin-like growth factor 1 levels by 117% (P < .001) and reduced body fat by 7.4% (P < .001). Adverse events were mild, reported by 68% of tesamorelin-treated adults. These findings suggest the potential of tesamorelin in enhancing cognitive function in both healthy older adults and those with MCI, warranting further investigation into its therapeutic role in brain health during aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3764914/.
Available from https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02572323.
Phase II Trial of Tesamorelin for Cognition in Aging HIV-Infected Persons
This study aims to investigate whether tesamorelin, in combination with a motivational text-messaging application, can improve memory and thinking in HIV-infected individuals experiencing abdominal fat accumulation. One hundred volunteers will be enrolled from two sites, with evidence of abdominal obesity and cognitive difficulties. Using a randomized trial design, participants will receive either tesamorelin or no treatment initially, with subsequent crossover. Memory and thinking skills will be assessed before and after treatment, alongside safety monitoring through blood tests and magnetic resonance scans of the head and abdomen.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02572323.
Friedman SD, Baker LD, Borson S, et al. Growth hormone-releasing hormone effects on brain γ-aminobutyric acid levels in mild cognitive impairment and healthy aging. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70(7):883-890. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.1425.
Growth hormone-releasing hormone effects on brain γ-aminobutyric acid levels in mild cognitive impairment and healthy aging
This study investigates the neurochemical effects of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) in adults, including those with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), through a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled substudy. Participants received daily injections of tesamorelin or placebo for 20 weeks, with brain magnetic resonance spectroscopy and cognitive testing conducted at baseline, week 10, and week 20. GHRH administration increased γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels in all brain regions, N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) levels in the frontal cortex, and decreased myo-inositol (MI) levels in the posterior cingulate, with no significant changes in glutamate levels. These findings suggest a potential mechanism for the cognitive benefits observed with GHRH treatment.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3764915/.
Clemmons DR, Miller S, Mamputu JC. Safety and metabolic effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0179538. Published 2017 Jun 15. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0179538.
Safety and metabolic effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The objective of this 12-week randomized, placebo-controlled study involving 53 patients with type 2 diabetes was to assess whether tesamorelin, a stabilized growth hormone-releasing hormone analogue, affects insulin sensitivity or diabetes control. Results showed no significant differences between groups in relative insulin response, fasting glucose levels, glycosylated hemoglobin, or overall diabetes control at Week 12. Relevant modifications in diabetes medications were similar between groups, and no patients discontinued the study due to loss of diabetes control. However, tesamorelin 2 mg treatment resulted in significant reductions in total cholesterol and non-HDL cholesterol compared to placebo.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5472315/.
Maggi P, Di biagio A, Rusconi S, et al. Cardiovascular risk and dyslipidemia among persons living with HIV: a review. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(1):551.
Cardiovascular risk and dyslipidemia among persons living with HIV: a review
This review aims to address the cardiovascular risk in individuals living with HIV and the appropriate antiretroviral therapy to mitigate this risk. Lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation, increased physical activity, and healthy dietary practices, are crucial in preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD). Statins play a central role in managing hypercholesterolemia and may have additional anti-inflammatory effects. However, differences in guidelines between regions underscore the need for specific recommendations tailored to HIV-infected patients. Other drugs like ezetimibe, fibrates, and experimental classes are also being explored. Additionally, the toxicity profiles of different antiretrovirals should be considered, with newer regimens showing improved tolerability. Lipodystrophy and dyslipidemia are significant concerns, highlighting the importance of ongoing research and the introduction of new therapies to address these long-term toxicities.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5550957/.
Available from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa072375.
Stanley TL, Falutz J, Marsolais C, Morin J, Soulban G, Mamputu JC, Assaad H, Turner R, Grinspoon SK. Reduction in visceral adiposity is associated with an improved metabolic profile in HIV-infected patients receiving tesamorelin. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Jun;54(11):1642-51. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis251. Epub 2012 Apr 10. PMID: 22495074; PMCID: PMC3348954.
Reduction in visceral adiposity is associated with an improved metabolic profile in HIV-infected patients receiving tesamorelin
Tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing hormone analogue, has shown to reduce visceral adipose tissue (VAT) in individuals with HIV-associated abdominal adiposity. In two phase III studies, responders with ≥8% reduction in VAT demonstrated significantly improved triglyceride levels, adiponectin levels, and glucose homeostasis compared to nonresponders. These findings highlight the potential metabolic benefits of tesamorelin treatment in HIV-infected patients.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3348954/.
Available from https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02196831.
Tesamorelin Effects on Liver Fat and Histology in HIV
Liver disease, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is prevalent in individuals with HIV infection, affecting approximately 30-40% of patients. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a severe form of NAFLD, is characterized by liver fat accumulation, inflammation, cellular damage, and fibrosis. NAFLD is more common in those with increased visceral adiposity, often associated with decreased growth hormone secretion in HIV-infected individuals. Tesamorelin, an FDA-approved growth hormone releasing hormone analogue, has shown promise in reducing visceral fat in HIV-infected patients. This study aims to investigate tesamorelin’s impact on liver fat and steatohepatitis in HIV-infected individuals with NAFLD, hypothesizing that it will decrease liver fat and alleviate associated inflammation, fibrosis, and hepatocellular damage.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02196831..
Fourman LT, Czerwonka N, Feldpausch MN, et al. Visceral fat reduction with tesamorelin is associated with improved liver enzymes in HIV. AIDS. 2017;31(16):2253–2259. doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000001614.
Visceral fat reduction with tesamorelin is associated with improved liver enzymes in HIV
The objective of this study was to assess whether tesamorelin-induced reductions in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) among HIV-infected individuals correlate with changes in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels. Analyzing data from two Phase III trials involving 806 HIV-infected patients with abdominal obesity, the majority of whom were VAT responders, we found that VAT reduction was associated with decreased ALT and AST levels in participants with elevated baseline transaminases. VAT responders showed greater reductions in ALT and AST compared to nonresponders after 26 weeks of treatment, and this improvement persisted over 52 weeks, even in those switched to placebo, despite some VAT reaccumulation.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5633509/.
Miller K, Halow J, Koretsky AP. Phosphocreatine protects transgenic mouse liver expressing creatine kinase from hypoxia and ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1993;265(6 Pt 1):C1544-51.
Phosphocreatine protects transgenic mouse liver expressing creatine kinase from hypoxia and ischemia
Creatine kinase (CK) is typically abundant in muscle and brain but not in the liver. By studying transgenic mice expressing high levels of CK in the liver, researchers have examined CK’s role during low oxygen stress. In normal liver ischemia, ATP levels decrease, and pH drops to 6.6, recovering post-reperfusion. However, transgenic livers maintain ATP levels until phosphocreatine (PCr) depletion, and pH remains stable during ischemia. Hypoxia in normal livers depletes ATP and increases lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, while transgenic livers maintain ATP levels and show no LDH increase for up to 90 minutes. These findings highlight CKB’s role in regulating ATP and pH during low oxygen stress.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.6.C1544?rfr_dat=cr_pub++0pubmed&url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org.
Spooner LM, Olin JL. Tesamorelin: a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue for HIV-associated lipodystrophy. Ann Pharmacother. 2012;46(2):240-7.
Tesamorelin: a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue for HIV-associated lipodystrophy
The objective was to assess the effectiveness and safety of tesamorelin for treating lipodystrophy associated with HIV infection. Literature was gathered from databases and additional sources, focusing on trials involving humans. Analysis of two Phase 3 trials and their pooled data revealed that tesamorelin significantly reduced waist circumference and visceral adipose tissue over 26 weeks, with sustained benefits in extension phases. Limited off-label uses were also noted. Tesamorelin offers a viable option for managing HIV-associated lipodystrophy, but considerations include cost and long-term safety.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1345/aph.1Q629?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed.
Mahdy Ali K, Wonnerth A, Huber K, Wojta J. Cardiovascular disease risk reduction by raising HDL cholesterol–current therapies and future opportunities. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;167(6):1177–1194. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02081.x.
Cardiovascular disease risk reduction by raising HDL cholesterol–current therapies and future opportunities
Since the 1950s, research on high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) has focused on its life cycle, role in atherosclerosis, and therapeutic modification. Studies like the Framingham study highlighted HDL-C as an independent cardiovascular risk factor, with even modest increases linked to risk reduction. Despite the success of statin therapy in lowering low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) and reducing coronary heart disease, cardiovascular events persist, prompting the search for new strategies. However, achieving substantial HDL-C increase with existing therapies remains challenging, and the focus has shifted towards understanding HDL particle functionality. This review explores current and emerging therapeutic options, discusses recent studies, and offers insights into future diagnostic and treatment approaches for coronary artery disease.
You can read the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3504986/.
Tuffaha SH, Singh P, Budihardjo JD, et al. Therapeutic augmentation of the growth hormone axis to improve outcomes following peripheral nerve injury. Expert OpinTher Targets. 2016;20(10):1259-65.
Therapeutic augmentation of the growth hormone axis to improve outcomes following peripheral nerve injury
Introduction: Peripheral nerve injuries often lead to significant motor and sensory impairments, with limited therapeutic options available for enhancing the regenerative process. Following surgical repair, axons must traverse long distances to reconnect with distal targets, while denervated muscle and Schwann cells undergo atrophy, hindering successful reinnervation. Growth hormone (GH)-based therapies offer potential to accelerate axonal regeneration and mitigate muscle and pathway atrophy before reinnervation. In this review, we explore the mechanisms underlying GH-based therapies’ effects on peripheral nerve regeneration, highlighting translational studies and potential secondary benefits such as improved bone, tendon, and wound healing. GH-based treatments show promise due to their multi-modal action, suggesting potential for clinical translation aided by existing FDA-approved drugs targeting the GH axis.
You can read the abstract of the article at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22298602/.
Patient Success Stories

Before
After

At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health.
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer

Before
After

I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics. Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old Actress (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
Free Consultation
Start Your Journey to a Younger, Healthier You!
Categories
Information
Free Consultation
STEPS AWAY FROM A YOUNGER. HEALTHIER YOU!
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have








