Peptides
- 5-amino-1MQ
- Aminophylline
- Aniracetam
- ARA 290
- Argireline + Leuphasyl
- BPC-157
- Bremelanotide
- Cerebrolysin
- CJC-1295
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Dihexa
- Elampretide (SS-31)
- Epithalon
- FG Loop Peptide (FGL)
- GHK-Cu
- Ginsenoside Rg3
- Glycyrrhetinic Acid
- Ipamorelin
- Kisspeptin
- KPV
- LL-37
- Melanotan 1
- Melanotan 2
- Mitochondrial ORF of the twelve S c (MOTS-c)
- MK-677 (IBUTAMOREN)
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
- Nicotinamide Riboside
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
- Noopept
- Pegylated Mechano Growth Factor
- Selank
- Semax
- Sermorelin
- SRT2104
- Tesamorelin
- Thymosin Alpha 1
- Thymosin Beta 4
- Tiger 17
- Valproic Acid
- Valproic acid + PTD-DBM
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Zinc-Thymulin
- Potential Health Benefits of Roflumilast
- Key Takeaways
- What is Roflumilast?
- How Roflumilast Works?
- Chemical Structure of Roflumilast
- Research on Roflumilast
- Roflumilast Side Effects
- Roflumilast drug class
- Roflumilast indications
- Roflumilast brand name
- Roflumilast dose
- Roflumilast copd guidelines
- Roflumilast mechanism
- Roflumilast vs montelukast
- Roflumilast vs theophylline
- Roflumilast drug interactions
- Roflumilast psoriasis
- FAQ
- References
Table of Contents
- Potential Health Benefits of Roflumilast
- Key Takeaways
- What is Roflumilast?
- How Roflumilast Works?
- Chemical Structure of Roflumilast
- Research on Roflumilast
- Roflumilast Side Effects
- Roflumilast drug class
- Roflumilast indications
- Roflumilast brand name
- Roflumilast dose
- Roflumilast copd guidelines
- Roflumilast mechanism
- Roflumilast vs montelukast
- Roflumilast vs theophylline
- Roflumilast drug interactions
- Roflumilast psoriasis
- FAQ
- References
Potential Health Benefits of Roflumilast
Roflumilast benefits include reducing inflammation, decreasing the frequency of COPD exacerbations, and improving symptoms of plaque psoriasis. It may also help lower alcohol consumption by modulating brain signaling pathways.
- Treats COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) [1-20]
- Treats asthma [21-31]
- Improves cognitive function [32-49]
- Reduces overall body fat [13-20, 50-53]
- Maintains bone strength and quality [54]
- Improves blood sugar levels [51, 55-60]
- Improves bladder function [61-62]
- Treats and prevents cancer [63-71]
Decreases alcohol consumption [72-73]
Key Takeaways
- Mechanism: Roflumilast is a selective phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor that reduces inflammation by increasing cAMP levels.
- Primary Use: It is mainly used to decrease the risk of exacerbations in patients with severe COPD associated with chronic bronchitis.
- Additional Use: Topical roflumilast (Zoryve) is FDA-approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include weight loss, diarrhea, nausea, headache, and potential psychiatric effects like depression.
- Emerging Research: Roflumilast may also help reduce alcohol consumption by modulating brain reward pathways.
What is Roflumilast?
Roflumilast is a drug that acts as a selective, long-acting inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase-4. It works by reducing the swelling in the lungs. It is commonly used for the treatment of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a group of diseases that affect your lungs and airways.
How Roflumilast Works?
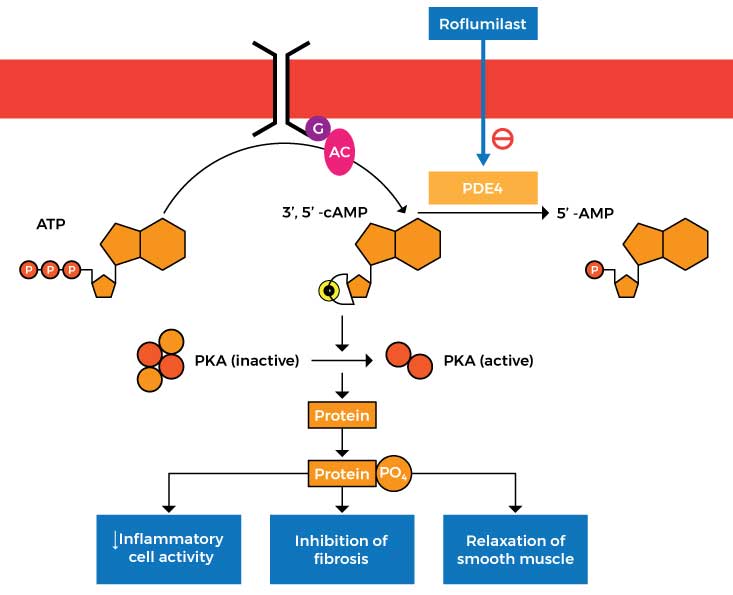
Roflumilast works by inhibiting an enzyme called phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) which in turn prevents the breakdown of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) into its inactive state (called AMP). This process decreases cell inflammation, inhibits fibrosis (thickening or scarring of the tissue), and relaxes the smooth muscle in the lungs.
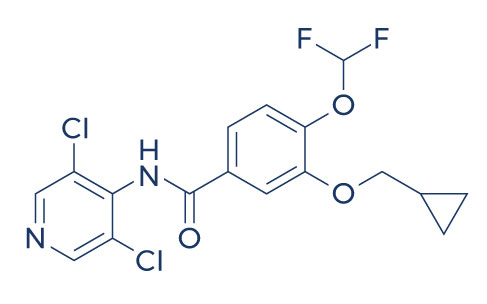
Chemical Structure of Roflumilast
Research on Roflumilast
A. Treats COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)

Roflumilast treats COPD by inhibiting the enzyme phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), which leads to an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP levels and a reduction in the production of inflammatory mediators. This anti-inflammatory effect helps decrease airway inflammation, reduce mucus production, and prevent the worsening of symptoms, ultimately lowering the frequency of COPD exacerbations, especially in patients with severe COPD associated with chronic bronchitis.
- A review of studies showed that roflumilast was safe and effective in treating COPD. [1]
- In patients with severe to very severe COPD associated with chronic bronchitis, roflumilast was effective in preventing the worsening of the condition (exacerbation). [2]
- In COPD patients, roflumilast successfully shifted the patients to a more stable state. [3]
- In patients with severe COPD and chronic bronchitis, roflumilast reduced the worsening of the condition and lowered the frequency of hospitalizations. [4]
- In COPD patients with a high risk of exacerbations, roflumilast administration prevented the worsening of symptoms. [5]
- A review of studies found that roflumilast improved lung function and reduced exacerbations among COPD patients via inhibition of airway inflammation. [6]
- A study showed that roflumilast was safe and effective for controlling COPD exacerbations. [7]
- In severe COPD patients not controlled by inhaled combination therapy, the addition of roflumilast reduced the prevalence of exacerbations. [8]
- In Asian COPD patients, roflumilast played an important role in improving lung function. [9]
- A review of studies confirmed the benefits of roflumilast in reducing the incidence of exacerbations in COPD patients. [10]
- In Korean COPD patients, roflumilast significantly improved lung function with a tolerable safety profile. [11]
- In chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients, roflumilast treatment resulted in improvements in exercise tolerance. [12]
- In patients with severe airflow limitation, bronchitic symptoms, and a history of COPD exacerbations, the administration of roflumilast was associated with significant improvements in measures of lung function. [13-20]
B. Treats Asthma

Roflumilast is not typically used to treat asthma because it is primarily approved for COPD; however, its mechanism as a phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor theoretically benefits asthma by reducing airway inflammation. By increasing intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels, roflumilast decreases the release of inflammatory mediators that contribute to airway hyperresponsiveness and obstruction in asthma. Although it shows anti-inflammatory effects that could help asthma symptoms, clinical trials have not consistently demonstrated enough benefit to warrant widespread use or FDA approval for asthma management.
- In asthma patients, roflumilast attenuated allergen-induced bronchoconstriction (narrowing of the airways) by reducing the levels of inflammatory mediators such as eosinophils and neutrophils. [21]
- In asthmatic patients, the administration of 100, 250, and 500 micrograms of roflumilast once daily for 12 weeks resulted in significant improvements in morning and evening peak expiratory flow (a measure of lung function). [22]
- A review of studies showed that roflumilast was well tolerated by asthma patients and was associated with symptom relief. [23]
- In patients with mild to moderate asthma, roflumilast significantly improved the symptoms. [24]
- A review of studies showed that roflumilast can help treat asthma through its anti-inflammatory properties. [25]
- In asthmatic mice, the combined treatment with roflumilast and fluticasone significantly improved the symptoms of asthma. [26]
- In a murine model of chronic asthma, roflumilast produced beneficial effects by regulating airway inflammation, airway hyper-responsiveness (AHR), and airway remodeling. [27]
- A study showed that roflumilast can help treat the symptoms of COPD and asthma. [28]
- In patients with moderate-to-severe asthma, the combined treatment of roflumilast with montelukast resulted in improved lung function and asthma control. [29]
- In asthmatic patients, daily oral administration of roflumilast was effective in improving pulmonary function and asthma symptoms. [30]
- In patients with mild asthma, roflumilast attenuated allergen-induced AHR. [31]
C. Improves Cognitive Function

Roflumilast improves cognitive function by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), an enzyme that breaks down cyclic AMP (cAMP) in the brain. By increasing cAMP levels, roflumilast enhances signaling pathways involved in memory, learning, and neuroplasticity. This boost in cAMP activity can lead to better synaptic function and reduced neuroinflammation, both of which are critical for cognitive performance. Research has shown that roflumilast may improve working memory, attention, and executive function, especially in conditions associated with cognitive decline.
- In rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage (bleeding in the space between the brain and the surrounding membrane), roflumilast administration significantly improved neurological deficits. [32]
- In a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), roflumilast significantly ameliorated cognitive impairment. [33]
- In mice with insufficient blood flow to the brain, roflumilast demonstrated neuroprotective effects by decreasing nerve inflammation. 34]
- In rodents, roflumilast improved memory compared to rolipram, an anti-depressant. [35]
- In aged rats subjected to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (decreased blood flow to the brain), roflumilast promoted memory recovery and attenuated white matter injury. [36]
- In rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) models, roflumilast prevented ischemic stroke-induced neuronal damage by reducing oxidative stress. [37]
- In AD mice, roflumilast was successful in improving learning and memory. [38]
- In rats, the combined administration of roflumilast and tadalafil resulted in memory enhancement. [39]
- In rats with transient global cerebral ischemia (TGCI), roflumilast exhibited protective effects against TGCI-induced memory impairments. [40]
- In schizophrenia patients (a mental disorder that affects thinking, emotion, and reality perception), roflumilast treatment resulted in significant improvement in verbal memory. [41]
- In rats, roflumilast ameliorated hypertension-induced learning and memory impairments. [42]
- In AD mice, roflumilast was effective in alleviating memory loss and depression. [43]
- In juvenile rats, roflumilast reduced cellular damage in the brain caused by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. [44]
- In rat brains, roflumilast significantly decreased elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-a, IFN-?, and NF-?B. [45]
- In healthy young humans, roflumilast was potentially effective for treating disorders affected by disrupted sensory gating. [46]
- In patients with schizophrenia, roflumilast treatment was associated with improvement in attention. [47]
- In young and elderly humans with acute brain injury, roflumilast treated residual cognitive deficits. [48]
- In rats, roflumilast prevented memory deficits caused by sleep deprivation. [49]
D. Reduces Overall Body Fat

Roflumilast helps maintain bone strength and quality by reducing inflammation through inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), which decreases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that can lead to bone resorption. Chronic inflammation is known to stimulate osteoclast activity, weakening bones over time. By controlling this inflammatory response, roflumilast may help preserve bone density and structural integrity, offering potential benefits for long-term skeletal health.
- In patients with COPD, roflumilast administration was associated with weight loss. [13-20]
- In obese adults with prediabetes, roflumilast was associated with fat mass loss. [50]
- In mice, roflumilast administration resulted in the reduction of body weight gain. [51]
- A study showed that roflumilast can help address obesity-related diseases by suppressing the formation of fat cells. [52]
- In obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), short-term monotherapy with roflumilast was associated with significant weight loss. [53]
E. Maintains Bone Strength and Quality

Roflumilast helps maintain bone strength and quality by reducing inflammation through inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), which decreases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that can lead to bone resorption. Chronic inflammation is known to stimulate osteoclast activity, weakening bones over time. By controlling this inflammatory response, roflumilast may help preserve bone density and structural integrity, offering potential benefits for long-term skeletal health.
- In rats with ligature-induced periodontitis (inflammation of the gums and bone surrounding and supporting the teeth), roflumilast was found to decrease alveolar bone loss. [54]
F. Improves Blood Sugar Levels

Roflumilast may improve blood sugar levels by reducing inflammation, which plays a major role in insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism. As a PDE4 inhibitor, roflumilast increases intracellular cAMP, leading to decreased production of inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, both of which are associated with worsening blood sugar control. By lowering systemic inflammation, roflumilast can enhance insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood glucose levels more effectively, offering potential benefits for individuals with metabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes.
- In mice fed with a high-fat Western-type diet, roflumilast treatment reduced weight gain by increasing energy expenditure and led to improved glucose metabolism. [51]
- In type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, roflumilast administration resulted in lower blood sugar levels. [55]
- In mice, oral administration of roflumilast successfully delayed the progression of diabetes. [56]
- In COPD patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus, roflumilast treatment improved results in tests that measure blood sugar levels such as fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c (glycated hemoglobin). [57]
- In diabetic rats with elevated blood sugar levels, roflumilast administration at 2 and 3 mg/kg protected against diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage). [58]
- In patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus, roflumilast administration at a dose of 500 µg once daily resulted in a greater reduction in glycated hemoglobin. [59]
- In patients with COPD with metabolic syndrome, long-term administration of roflumilast in addition to traditional treatment improved blood sugar levels. [60]
G. Improves Bladder Function

Roflumilast may improve bladder function by reducing inflammation through its inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), which leads to increased levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in tissues. Elevated cAMP can relax smooth muscle, decrease inflammatory signaling, and enhance nerve signaling pathways involved in bladder control. As a result, roflumilast may help improve symptoms like overactive bladder, urinary frequency, and urgency by promoting better coordination between the bladder muscle and the nervous system.
- In rats with diabetic bladder dysfunction, oral treatment with roflumilast for 6 weeks improved bladder function and inhibited the production of inflammatory factors. [61]
- In rats with obesity-associated overactive bladder, roflumilast treatment for 12 weeks restored normal bladder function via inhibition of bladder inflammation. [62]
H. Treats and Prevents Cancer

Roflumilast may help treat and prevent cancer by inhibiting the enzyme phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), which plays a role in promoting inflammation, cell proliferation, and survival — all processes that can contribute to cancer development. By blocking PDE4, roflumilast increases intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels, leading to reduced inflammatory signaling and potentially inducing cancer cell apoptosis (programmed cell death). Early studies suggest it may slow the growth of certain tumors, particularly those linked to chronic inflammation, such as lung cancer, but more research is needed to fully establish its role in cancer therapy.
- In a murine lung cancer model, roflumilast inhibited the growth of lung cancer cells. [63]
- A cell study showed that roflumilast inhibited ovarian cancer cell growth and spread by inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death) and cell cycle arrest. [64]
- In lung cancer patients, combination treatments with roflumilast and anti-cancer medications produced increased apoptosis. [65]
- In patients with cancer of the lymphatic system, the addition of roflumilast to chemotherapy was associated with increased inhibition of cancer cells and improved survival rate. [66]
- A cell study found that roflumilast enhanced the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to the chemotherapeutic agent cisplatin. [67]
- In rats with prostate cancer, roflumilast enhanced the cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of cisplatin. [68]
- In rats with colon cancer, roflumilast restored the normal architecture of the colonic mucosa via inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress. [69]
- In patients with advanced beta cell malignancies, the administration of oral roflumilast at a dose of 500 mcg daily for 21 days with prednisone on days 8 to 14 inhibited the growth and spread of cancer cells. [70]
- In patients with liver cancer, roflumilast suppressed the progression of cancer cells. [71]
I. Decreases Alcohol Consumption

Roflumilast decreases alcohol consumption by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), which leads to increased levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in the brain. Higher cAMP levels help regulate the reward pathways and reduce the reinforcing effects of alcohol, thereby decreasing cravings and the desire to drink. This modulation of brain signaling pathways involved in addiction suggests that roflumilast could be a promising therapeutic option for individuals with alcohol use disorder.
- In a mouse model of alcoholism, roflumilast treatment decreased ethanol intake and preference. [72]
- In mice with alcoholism treated with roflumilast (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg), a significant reduction in ethanol intake and preference was observed. [73]
Roflumilast Side Effects
Roflumilast side effects are very uncommon. There have been some side effects associated with the use of this drug wherein the patient had one of the issues listed below at some point while being on roflumilast. However, these side effects weren’t confirmed to be associated with the treatment and could have been a coincidence and not related to the use of roflumilast. Despite this, it was listed as a side effect associated with roflumilast even though these associated side effects are very uncommon.
Side effects associated with roflumilast may include the following:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle pain
- Nausea
- Palpitation
Roflumilast drug class
Roflumilast belongs to a class of drugs known as phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitors. This class works by inhibiting the PDE4 enzyme, which is involved in the breakdown of cyclic AMP (cAMP), a molecule that plays a key role in regulating inflammation. By increasing cAMP levels, roflumilast helps reduce the inflammation in the lungs associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other respiratory conditions.
As a PDE4 inhibitor, roflumilast is primarily used to manage COPD, particularly in patients with a history of frequent flare-ups. It helps to decrease inflammation, relax airway muscles, and reduce the production of mucus, which can improve lung function and overall breathing. It is often prescribed in combination with other medications to enhance its therapeutic effects.
Roflumilast’s drug class also includes treatments for various inflammatory conditions, though its specific use in COPD is one of its most common applications. While it is not a bronchodilator, its role in inflammation control provides a complementary effect when used alongside other respiratory medications like beta-agonists and corticosteroids.
Roflumilast indications
Roflumilast is primarily indicated for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It works as a phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, reducing inflammation in the lungs and helping to prevent exacerbations in patients with severe COPD. Roflumilast is typically prescribed as an adjunct to bronchodilator therapy in patients who experience frequent COPD flare-ups despite other treatments.
Additionally, roflumilast has shown efficacy in managing conditions associated with chronic inflammatory processes. It is sometimes used off-label to address other inflammatory disorders, such as psoriasis or conditions involving excessive inflammation. However, its use outside of COPD remains less common and requires careful consideration by healthcare providers.
Roflumilast is also being investigated for its potential role in reducing alcohol consumption. Research suggests that it may help decrease cravings and the desire for alcohol, making it a possible treatment for alcohol use disorder. Although not yet a standard indication, early findings show promise for roflumilast in this area, potentially expanding its therapeutic applications in the future.
Roflumilast brand name
Roflumilast is marketed under the brand name Daliresp, primarily used to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). As a selective phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, it helps reduce inflammation and relax the airways, making breathing easier for those with COPD. The brand name Daliresp is widely recognized in the healthcare community for its role in managing COPD symptoms.
Daliresp is typically prescribed when other medications, such as bronchodilators, are not enough to control COPD symptoms. The medication works by reducing the number of flare-ups and preventing long-term damage to the lungs, improving overall lung function. While it is not a rescue medication, it is part of an ongoing treatment plan aimed at reducing COPD progression.
In addition to its use for COPD, studies have shown that Roflumilast under the brand name Daliresp has other potential benefits, such as decreasing alcohol consumption in individuals with alcohol use disorder. This dual effect of reducing both inflammation in the lungs and cravings for alcohol highlights the versatility of the drug in managing different health conditions.
Roflumilast dose
Roflumilast is typically prescribed in a dose of 500 micrograms once daily for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is taken orally in the form of a tablet, and the dosage remains consistent throughout the treatment course. It is important to take Roflumilast at the same time each day to help maintain a routine and ensure optimal therapeutic effects.
The dose may need to be adjusted in certain circumstances. For example, individuals with moderate to severe liver impairment may require a lower dose or should avoid using the medication altogether. It’s essential for healthcare providers to assess each patient’s specific health status and adjust the dosage accordingly to minimize side effects and ensure safety.
Patients should follow their doctor’s instructions carefully when taking Roflumilast. If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it is almost time for the next dose. Doubling up on doses to make up for missed ones is not recommended, as it can increase the risk of side effects. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing the medication.
Roflumilast copd guidelines
Roflumilast is recommended in the 2024 GOLD guidelines as an oral once-daily PDE4 inhibitor for patients with severe to very severe COPD (post-bronchodilator FEV₁ < 50% predicted) who have a chronic bronchitis phenotype and a history of exacerbations; it has been shown to reduce the rate of moderate and severe exacerbations treated with systemic corticosteroids and to improve lung function when added to standard inhaled therapy.
In clinical practice, roflumilast is positioned as an add-on to long-acting bronchodilators—particularly in patients whose symptoms and exacerbation frequency remain uncontrolled on LABA + LAMA or LABA + ICS combinations—and may offer the greatest benefit in those with a recent hospitalization for acute exacerbation.
The recommended dosing regimen begins with 250 µg once daily for the first month, escalating to 500 µg once daily thereafter; clinicians should monitor for common adverse effects such as diarrhea, nausea, weight loss and sleep disturbances, and avoid its use in underweight patients or those with a history of depression.
Roflumilast mechanism
Roflumilast is a selective phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor that works by blocking the action of this enzyme. PDE4 is involved in the breakdown of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), a molecule that plays a key role in regulating inflammation and immune responses. By inhibiting PDE4, roflumilast increases cAMP levels, which in turn reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other inflammatory mediators.
In the lungs, roflumilast’s mechanism helps to decrease inflammation associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This leads to improved airway function and reduced symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. By targeting the inflammatory pathways, roflumilast helps to control the chronic inflammatory response that drives COPD progression.
Additionally, roflumilast has been shown to influence the central nervous system, where it may have potential benefits in reducing alcohol consumption. Through the modulation of cAMP levels, it alters the neural pathways involved in alcohol cravings and consumption, which makes it useful in treating alcohol use disorders. This dual action, both in the lungs and the brain, makes roflumilast a promising therapeutic agent in various inflammatory and addiction-related conditions.
Roflumilast vs montelukast
Roflumilast and montelukast are both medications used to treat respiratory conditions, but they work through different mechanisms. Roflumilast is primarily used for managing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and works by inhibiting the enzyme phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), which reduces inflammation in the airways. This helps prevent exacerbations and improves lung function in individuals with COPD. On the other hand, montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist that helps manage asthma and allergic rhinitis by blocking the action of leukotrienes, which are chemicals in the body that contribute to inflammation and constriction of the airways.
While both medications target inflammation, they differ in their specific uses and how they are prescribed. Roflumilast is typically reserved for patients with severe COPD and is often used alongside other treatments like bronchodilators and corticosteroids. Montelukast, however, is more commonly used for asthma control, especially in patients with allergic triggers or exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. It is also used for children with asthma and seasonal allergies, making it a more versatile option in asthma management.
In terms of side effects, roflumilast may cause gastrointestinal issues, weight loss, and psychiatric symptoms, which can be significant drawbacks for some patients. Montelukast, while generally well-tolerated, has been linked to rare cases of mood changes and behavior problems, particularly in children. The choice between roflumilast and montelukast depends on the specific condition being treated, the severity of symptoms, and the individual patient’s health profile.
Roflumilast vs theophylline
Roflumilast and theophylline are both medications used to manage respiratory conditions, particularly chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, they work in different ways to achieve similar goals. Roflumilast is a selective phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, primarily used to reduce inflammation in the airways, decrease exacerbations, and improve lung function. It targets the underlying inflammation seen in COPD, making it effective in preventing flare-ups.
Theophylline, on the other hand, is a methylxanthine drug that works by relaxing the muscles of the airways and improving airflow. It also has anti-inflammatory effects, although its exact mechanism in this regard is less understood. Theophylline is more commonly used as a bronchodilator to relieve symptoms of wheezing and shortness of breath, but it can also have side effects, including nausea, arrhythmias, and toxicity, especially at higher doses.
While both medications aim to improve lung function, roflumilast is generally preferred for patients with more severe COPD or those with frequent exacerbations due to its anti-inflammatory properties. Theophylline, although effective in certain cases, is typically considered a second-line treatment due to its narrower therapeutic window and potential for side effects. The choice between these two medications often depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s individual response to treatment.
Roflumilast drug interactions
Roflumilast can interact with several other medications, potentially affecting its efficacy or causing unwanted side effects. For instance, when taken alongside strong cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors like ketoconazole or ritonavir, roflumilast levels in the body may increase, raising the risk of side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and weight loss. It’s essential for healthcare providers to adjust the dose of roflumilast if it’s used concurrently with these medications.
Additionally, drugs that induce cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as rifampin or carbamazepine, may lower the effectiveness of roflumilast by increasing its breakdown in the body. This interaction could reduce the therapeutic benefits of roflumilast, making it less effective in managing conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Roflumilast may also interact with other medications that affect the immune system or the gastrointestinal system. For example, combining it with corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive drugs might heighten the risk of infections. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking to prevent any potential interactions and ensure safe and effective treatment.
Roflumilast psoriasis
Roflumilast has shown potential in the treatment of psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition that causes rapid skin cell turnover and inflammation. As a phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, roflumilast works by reducing the inflammatory response, which plays a key role in psoriasis flare-ups. This mechanism helps to alleviate the symptoms, including redness, scaling, and thickened skin.
Studies suggest that roflumilast may be beneficial for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis, especially those who haven’t responded well to traditional treatments like topical steroids or phototherapy. By targeting the underlying inflammatory pathways, it can offer an alternative for managing the condition, particularly for those seeking oral therapies.
While roflumilast is primarily used for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), its effectiveness in treating psoriasis highlights its broader therapeutic potential. However, like all medications, it should be prescribed and monitored by healthcare professionals due to the possibility of side effects and varying patient responses.
FAQ
What type of medication is roflumilast?
Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor used to reduce inflammation and may also have potential benefits in conditions associated with inflammation, such as a urinary tract infection. Its half-life is relatively long, allowing for once-daily dosing, and this extended half-life helps maintain stable drug levels in the body.
Does roflumilast contain steroids?
No, roflumilast does not contain steroids, but it may cause side effects such as decreased appetite and breathing problems. In some cases, breathing problems may become more noticeable, particularly in patients with pre-existing lung conditions.
Why is roflumilast used in COPD?
Roflumilast is used in COPD to decrease inflammation in the lungs and reduce the frequency of exacerbations, although certain factors can increase roflumilast systemic exposure.
What is the adverse effect of roflumilast?
A significant adverse effect of roflumilast is weight loss, and patients with certain medical conditions should be closely monitored. Additionally, they should be advised on what to do in case of a missed dose, particularly those with pre-existing medical conditions.
What are 5 side effects of drugs?
Common side effects of roflumilast include diarrhea, nausea, weight loss, headache, and insomnia; if a missed dose occurs, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it is almost time for the next dose.
What is the warning for roflumilast?
Roflumilast carries a warning for an increased risk of psychiatric events, including depression and suicidal thoughts, and it is important to consider potential drug interactions when prescribing it.
What is the best time to take roflumilast?
Roflumilast is typically taken once daily, with or without food, at the same time each day, but caution is advised in patients with liver disease, especially in those with affected areas of impaired liver function. Additionally, it is important to monitor for any side effects in the affected areas of the body, particularly the gastrointestinal system.
Is roflumilast a steroid?
No, roflumilast is not a steroid, but it can increase systemic exposure to its active metabolites. Roflumilast is being studied for its potential benefits in treating atopic dermatitis, due to its anti-inflammatory properties. Early research suggests that roflumilast may help manage atopic dermatitis symptoms by targeting underlying inflammation, offering a non-steroidal option for patients with atopic dermatitis.
Is roflumilast a PDE4 inhibitor?
Yes, roflumilast is a selective PDE4 inhibitor that can increase systemic exposure by inhibiting the breakdown of cAMP. Systemic exposure to the drug enhances its anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body. However, increased systemic exposure may also raise the risk of side effects and requires careful monitoring.
Is roflumilast an anti-inflammatory drug?
Yes, roflumilast acts as an anti-inflammatory drug by reducing inflammatory mediators, which can increase systemic exposure to its therapeutic effects. However, it’s important to be cautious when using herbal products alongside roflumilast, as some herbal products may interact with the medication and affect its efficacy.
Does roflumilast affect the kidneys?
Roflumilast is primarily metabolized by the liver and does not significantly affect kidney function; however, impaired liver function may lead to increased adverse reactions. Patients with liver impairment are at higher risk of increased adverse reactions due to reduced drug clearance. Therefore, caution is advised as increased adverse reactions may occur in vulnerable populations.
Is roflumilast the same as DALIRESP?
Yes, DALIRESP is the brand name for oral roflumilast used in COPD, and it is available in oral tablet form. The oral tablet form of DALIRESP makes it convenient for daily use in managing symptoms. Patients benefit from the oral tablet form due to its ease of administration and consistent dosing.
What kind of drug is roflumilast?
Roflumilast is an oral anti-inflammatory PDE4 inhibitor, but roflumilast cream is a topical formulation used for skin conditions like psoriasis. Unlike the oral form, roflumilast cream delivers targeted anti-inflammatory effects directly to the affected skin. Patients with plaque psoriasis may benefit from roflumilast cream as a non-steroidal treatment option, with most common side effects being local irritation or redness. For the oral form, the most common side effects include diarrhea, weight loss, and headache.
What is the risk of roflumilast?
Risks include psychiatric effects like depression, suicidal thoughts, weight loss, and gastrointestinal side effects. However, roflumilast cream is generally well-tolerated when used topically. Patients using roflumilast cream should still be monitored for systemic absorption risks, especially when applying roflumilast cream to large or damaged areas of skin.
What is the benefit of roflumilast?
The main benefit of roflumilast is the reduction of COPD exacerbations and inflammation, though some patients may experience trouble sleeping. Trouble sleeping is a known side effect that can affect treatment adherence. It’s important to monitor for trouble sleeping during roflumilast therapy and manage it appropriately. Additionally, patients should wash hands regularly to prevent infection and wash hands before taking any medication to ensure proper hygiene.
What are the indications for roflumilast?
Roflumilast is indicated for reducing the risk of COPD exacerbations and treating plaque psoriasis, but it may cause trouble sleeping in some patients. Individuals taking roflumilast should report any persistent trouble sleeping to their healthcare provider. Managing side effects like trouble sleeping can help improve treatment adherence and outcomes.
When do you consider roflumilast?
Roflumilast is considered for COPD patients with a history of frequent exacerbations and chronic bronchitis, especially when they adhere to a regular dosing schedule. A regular dosing schedule helps maintain consistent therapeutic levels, improving the medication’s effectiveness. For optimal results, patients should follow a regular dosing schedule as prescribed by their healthcare provider.
When would roflumilast be indicated for a COPD patient?
It is indicated for patients with severe COPD associated with chronic bronchitis and a history of exacerbations, especially those who may also have a history of mental health problems. Careful monitoring is necessary, as roflumilast can potentially exacerbate mental health problems, including depression and suicidal thoughts. Patients with existing mental health problems should be closely assessed before starting treatment.
What is roflumilast approved for?
Roflumilast is approved for reducing the risk of COPD exacerbations and treating plaque psoriasis (topically). Additionally, it may help some patients lose weight by reducing appetite and increasing energy expenditure, which could be beneficial in managing obesity-related conditions. As a result, individuals with COPD or psoriasis who are also looking to lose weight might find roflumilast helpful in their treatment plan.
How much does roflumilast cost?
The cost varies, but oral roflumilast (DALIRESP) can cost several hundred dollars per month without insurance, making it significantly more expensive than many over the counter alternatives. Some patients may look for over the counter treatments to manage symptoms, but these may not be as effective. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider, as over the counter options may not provide the same benefits as roflumilast.
Are Daliresp and roflumilast the same thing?
Yes, Daliresp is the brand name for oral roflumilast. It may interact with other medicines, so it’s important to inform your healthcare provider about any other medicines you are taking. Always consult your doctor before combining Daliresp with other medicines to avoid potential side effects or interactions.
What is the brand name for roflumilast topical?
The brand name for topical roflumilast is Zoryve, which may be used alongside other drugs to treat psoriasis. When using Zoryve, it’s important to consider interactions with other drugs that a patient may be taking. Always consult a healthcare provider to ensure that Zoryve does not interfere with the effects of other drugs.
Who should not take roflumilast?
Patients with moderate to severe liver impairment and those with a history of depression or suicidal behavior should not take roflumilast. It is important to refer to the medication guide for detailed information on contraindications and warnings. Always consult the medication guide before starting treatment to understand potential risks. Following the medication guide will ensure proper use and minimize adverse effects.
What should I monitor after giving roflumilast?
Monitor weight, mood changes, gastrointestinal symptoms, signs of infection, and interactions with herbal supplements, especially when taking 250 mcg of roflumilast. It is also important to check for any adverse effects if the dosage is adjusted to 250 mcg.
What is the gold first line treatment for COPD?
Long-acting bronchodilators (like LABAs or LAMAs) are the first-line treatment for COPD, as outlined in the prescribing information for these medications. However, individuals who plan to become pregnant should consult with their healthcare provider before starting these treatments, as alternative options may be recommended. If you plan to become pregnant, it is important to discuss potential risks and benefits with your doctor to ensure the safest approach to managing COPD.
What is the roflumilast mechanism of action?
In psoriasis, roflumilast reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the rapid turnover of skin cells, particularly during phase II of the inflammatory response. This can lead to other unusual changes in the skin’s appearance and texture. Additionally, roflumilast may cause other unusual changes in the body’s inflammatory processes, contributing to overall symptom relief.
How does roflumilast work in COPD?
It decreases inflammation in the airways, leading to fewer COPD exacerbations, as outlined in the prescribing information. However, roflumilast can cause serious side effects, including psychiatric issues and gastrointestinal disturbances. Patients should be monitored for serious side effects, particularly when starting treatment.
What is the mechanism of action of roflumilast in psoriasis?
In psoriasis, roflumilast reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the rapid turnover of skin cells, but it should be used cautiously in patients with liver problems due to the risk of other side effects. Additionally, other side effects such as gastrointestinal issues and mood changes may occur, requiring careful monitoring during treatment.
Can you take montelukast and roflumilast together?
Yes, they can be taken together if prescribed, but they should be monitored for additive side effects, especially to avoid any potential risks to the unborn baby. It is important to follow the prescription guidelines carefully to ensure safe use of both medications.
What are 5 side effects of drugs?
Common side effects of roflumilast include diarrhea, nausea, weight loss, headache, and insomnia; if a missed dose occurs, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it is almost time for the next dose.
What is the alternative to montelukast?
Alternatives to montelukast include inhaled corticosteroids, antihistamines, or leukotriene inhibitors like zafirlukast, which are available by prescription, as well as dual inhibitors targeting multiple inflammatory pathways, which also require a prescription.
Why is roflumilast not used in asthma?
Roflumilast is not approved for asthma due to insufficient evidence of benefit and concerns over side effects, unlike dual inhibitors that target multiple pathways in the inflammatory process. A prescription is required for its use, and it should only be taken under medical supervision with a valid prescription.
What is the difference between theophylline and roflumilast?
Theophylline is a bronchodilator and PDE inhibitor affecting multiple PDE types, while roflumilast is a selective PDE4 inhibitor with primarily anti-inflammatory effects when taken on a regular basis. For optimal results, both medications should be evaluated and monitored on a regular basis.
What are the interactions with roflumilast?
Roflumilast can interact with strong CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 inducers like rifampin and carbamazepine, reducing its effectiveness, which may also affect conditions like skin folds in some individuals. Patients should consult their doctor if they need to stop taking roflumilast due to reduced efficacy or side effects. In cases of severe interactions or adverse reactions, it may be necessary to stop taking roflumilast under medical supervision.
What drugs interact with DALIRESP?
Drugs like rifampin, phenobarbital, and carbamazepine can decrease DALIRESP levels and effectiveness, potentially exacerbating conditions like seborrheic dermatitis. Additionally, patients with seborrheic dermatitis may need to be monitored more closely when taking DALIRESP alongside these medications.
What are the contraindications for the drug roflumilast?
Contraindications include moderate to severe liver impairment and certain liver problems, a history of depression with suicidal behavior, and caution should be used in patients with psoriatic arthritis or those at risk for developing psoriatic arthritis, especially if they have certain liver problems.
Can roflumilast be used for psoriasis?
Yes, topical roflumilast is approved for treating plaque psoriasis, and animal studies have shown its effectiveness in reducing inflammation and skin cell turnover. Further animal studies are ongoing to explore its full therapeutic potential in dermatology.
What is roflumilast used for in dermatology?
It is used for treating plaque psoriasis to reduce inflammation and scaling, with roflumilast N oxide playing a key role in its anti-inflammatory effects. The metabolism of roflumilast into roflumilast N oxide is crucial for its therapeutic action in reducing psoriasis symptoms.
What is the brand name for roflumilast psoriasis?
The brand name for topical roflumilast for psoriasis is Zoryve, and it is important to note that roflumilast may pass into breast milk, so its use should be carefully considered for breastfeeding mothers. Always consult with a healthcare provider before using Zoryve while breastfeeding to ensure it is safe for both the mother and breast milk.
Is Zoryve FDA approved for psoriasis?
Yes, Zoryve is FDA-approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, and its effectiveness may be influenced by concomitant use with other topical treatments. It’s important to monitor for potential interactions when considering concomitant use with systemic therapies.
Reference
Reid DJ, Pham NT. Roflumilast: a novel treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Pharmacother. 2012 Apr;46(4):521-9. doi: 10.1345/aph.1Q646. Epub 2012 Mar 20. PMID: 22433610.
Roflumilast: a novel treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Pharmacother
Roflumilast is a safe and effective treatment option for patients with moderate-to-severe COPD, particularly those with chronic bronchitis and a history of exacerbations, offering modest improvements in lung function and reduced exacerbation rates. It is generally well tolerated, though side effects like diarrhea, nausea, headache, weight loss, and neuropsychiatric symptoms may occur.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22433610/.Wedzicha JA, Calverley PM, Rabe KF. Roflumilast: a review of its use in the treatment of COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:81-90. Published 2016 Jan 6. doi:10.2147/COPD.S89849.
Roflumilast: a review of its use in the treatment of COPD
Roflumilast, a selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, helps reduce systemic inflammation and the frequency of moderate to severe exacerbations in patients with severe COPD, especially those with chronic bronchitis. Clinical trials show it improves lung function and is most effective when used alongside long-acting bronchodilators.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4708192/.Wedzicha JA, Rabe KF, Martinez FJ, Bredenbröker D, Brose M, Goehring UM, Calverley PMA. Efficacy of roflumilast in the COPD frequent exacerbator phenotype. Chest. 2013 May;143(5):1302-1311. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-1489. PMID: 23117188.
Efficacy of roflumilast in the COPD frequent exacerbator phenotype
Roflumilast significantly reduces the risk of frequent COPD exacerbations, helping shift patients from a frequent to an infrequent exacerbator status over one year. This effect is consistent regardless of prior inhaled corticosteroid use or airflow limitation severity.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23117188/.Martinez FJ, Calverley PM, Goehring UM, Brose M, Fabbri LM, Rabe KF. Effect of roflumilast on exacerbations in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease uncontrolled by combination therapy (REACT): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015 Mar 7;385(9971):857-66. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62410-7. Epub 2015 Feb 13. PMID: 25684586.
Effect of roflumilast on exacerbations in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease uncontrolled by combination therapy (REACT): a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Roflumilast significantly reduces the risk of frequent COPD exacerbations, helping shift patients toward a more stable, infrequent exacerbator status. This effect is consistent across different levels of disease severity and independent of other COPD treatments.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25684586/.Yu T, Fain K, Boyd CM, Singh S, Weiss CO, Li T, Varadhan R, Puhan MA. Benefits and harms of roflumilast in moderate to severe COPD. Thorax. 2014 Jul;69(7):616-22. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-204155. Epub 2013 Dec 17. PMID: 24347460; PMCID: PMC4455881.
Benefits and harms of roflumilast in moderate to severe COPD
Roflumilast provides a net benefit primarily for COPD patients at high risk of severe exacerbations, particularly when the annual risk exceeds 22%. For most other patients, the benefit-harm balance is unfavorable, suggesting that its use should be tailored to individual risk profiles.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24347460/.Shen LF, Lv XD, Chen WY, Yang Q, Fang ZX, Lu WF. Effect of roflumilast on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ir J Med Sci. 2018 Aug;187(3):731-738. doi: 10.1007/s11845-018-1738-9. Epub 2018 Feb 3. PMID: 29397527.
Effect of roflumilast on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Roflumilast significantly improves lung function and reduces exacerbations in COPD patients by inhibiting airway inflammation. However, its use is associated with increased risks of side effects such as diarrhea and weight loss.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29397527/.Lipari M, Benipal H, Kale-Pradhan P. Roflumilast in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2013 Dec 1;70(23):2087-95. doi: 10.2146/ajhp130114. PMID: 24249758.
Roflumilast in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Roflumilast is an oral PDE-4 inhibitor approved for managing COPD, particularly in patients with severe disease, chronic bronchitis, and frequent exacerbations. It reduces exacerbations and improves lung function, but may cause side effects like diarrhea, weight loss, and psychiatric events.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24249758/.Calverley PM, Martinez FJ, Fabbri LM, Goehring UM, Rabe KF. Does roflumilast decrease exacerbations in severe COPD patients not controlled by inhaled combination therapy? The REACT study protocol. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2012;7:375-82. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S31100. Epub 2012 Jun 20. PMID: 22791991; PMCID: PMC3393336.
Does roflumilast decrease exacerbations in severe COPD patients not controlled by inhaled combination therapy? The REACT study protocol
The REACT study evaluates whether adding roflumilast to standard inhaled combination therapy further reduces COPD exacerbations in patients with severe disease and frequent flare-ups. Given its unique anti-inflammatory mechanism, roflumilast may offer additional benefits beyond current treatments.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22791991/.Zheng J, Yang J, Zhou X, Zhao L, Hui F, Wang H, Bai C, Chen P, Li H, Kang J, Brose M, Richard F, Goehring UM, Zhong N. Roflumilast for the treatment of COPD in an Asian population: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study. Chest. 2014 Jan;145(1):44-52. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-1252. PMID: 24135893.
Roflumilast for the treatment of COPD in an Asian population: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study
Roflumilast significantly improved lung function in patients with severe to very severe COPD in a predominantly Asian population and was well tolerated. The study supports its use as an effective treatment option across diverse ethnic groups.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24135893/.Martinez FJ, Rabe KF, Calverley PMA, Fabbri LM, Sethi S, Pizzichini E, McIvor A, Anzueto A, Alagappan VKT, Siddiqui S, Reisner C, Zetterstrand S, Román J, Purkayastha D, Bagul N, Rennard SI. Determinants of Response to Roflumilast in Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Pooled Analysis of Two Randomized Trials. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Nov 15;198(10):1268-1278. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2493OC. PMID: 29763572.
Determinants of Response to Roflumilast in Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Pooled Analysis of Two Randomized Trials
Roflumilast significantly reduces moderate to severe exacerbations in patients with severe COPD, particularly in those with prior hospitalizations, frequent exacerbations, or elevated baseline blood eosinophil counts (≥150 cells/μl). These findings help identify subgroups most likely to benefit from roflumilast therapy.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29763572/.Lee JS, Hong YK, Park TS, Lee SW, Oh YM, Lee SD. Efficacy and Safety of Roflumilast in Korean Patients with COPD. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(4):928-935. doi:10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.928.
Efficacy and Safety of Roflumilast in Korean Patients with COPD
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of roflumilast in Korean COPD patients, showing a significant improvement in lung function compared to placebo after 12 weeks, regardless of the severity of airflow limitation. While adverse events were more common in the roflumilast group, the safety profile was consistent with previous studies.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27189287/.Rogliani P, Ora J, Puxeddu E, Calzetta L, Cavalli F, Matera MG, Cazzola M. Effect of adding roflumilast or ciclesonide to glycopyrronium on lung volumes and exercise tolerance in patients with severe COPD: A pilot study. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Apr;49:20-26. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2017.12.010. Epub 2017 Dec 30. PMID: 29294360.
Effect of adding roflumilast or ciclesonide to glycopyrronium on lung volumes and exercise tolerance in patients with severe COPD: A pilot study
This pilot study explored the effects of adding oral roflumilast or inhaled ciclesonide to glycopyrronium in patients with severe COPD. The results showed that while glycopyrronium significantly improved lung function and exercise tolerance, adding roflumilast or ciclesonide provided no additional benefits in lung function or walking distance.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29294360/.Rabe K. F. (2011). Update on roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. British journal of pharmacology, 163(1), 53–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01218.x.
Update on roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Roflumilast, a selective PDE4 inhibitor, has been approved for the oral, once-daily treatment of severe COPD, demonstrating improvements in lung function and reduced exacerbation frequency. It works by targeting inflammatory processes in COPD and is effective when used alongside bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, offering a significant treatment option for patients with chronic bronchitis and persistent symptoms.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21232047/.American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Standards for the diagnosis and management of patients with COPD. 2004. [Accessed January 23, 2015]. Available from: http://www.thoracic.org/copd-guidelines/resources/copddoc.pdf.
Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Standards for the diagnosis and management of patients with COPD
You can read the abstract of this article at
Schols AM, Slangen J, Volovics L, Wouters EF. Weight loss is a reversible factor in the prognosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(6 Pt 1):1791–1797.
Weight loss is a reversible factor in the prognosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
The study examined the prognostic significance of body weight changes in COPD patients, revealing that low BMI and weight loss are independent predictors of increased mortality. In both retrospective and prospective analyses, weight gain and improved nutritional status were associated with better survival outcomes, suggesting that addressing low body weight through therapy may improve prognosis in COPD patients.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9620907/.Calverley PMA, Fabbri LM, Rabe KF, Mosberg H. Roflumilast in the treatment of COPD: a pooled safety analysis. Eur Respir J. 2010;36(Suppl 54) Abstract P4001.
Roflumilast in the treatment of COPD: a pooled safety analysis
COPD is a progressive condition characterized by chronic inflammation and airflow limitation, often leading to comorbidities and frequent exacerbations. Roflumilast, a selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, has been shown to reduce exacerbations and improve lung function, making it a beneficial treatment option for patients with severe COPD, particularly when used in combination with long-acting bronchodilators.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4708192/.Fabbri, L. M., Calverley, P. M., Izquierdo-Alonso, J. L., Bundschuh, D. S., Brose, M., Martinez, F. J., Rabe, K. F., & M2-127 and M2-128 study groups (2009). Roflumilast in moderate-to-severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with longacting bronchodilators: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet (London, England), 374(9691), 695–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61252-6.
Roflumilast in moderate-to-severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with longacting bronchodilators: two randomised clinical trials
Roflumilast improves lung function in patients with moderate-to-severe COPD who are already treated with salmeterol or tiotropium, as shown by significant increases in pre- and post-bronchodilator FEV1. While the drug was generally well-tolerated, it was associated with side effects like nausea, diarrhea, and weight loss, leading to increased patient withdrawals.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19716961/.Cilli A, Bal H, Gunen H. Efficacy and safety profile of roflumilast in a real-world experience. J Thorac Dis. 2019 Apr;11(4):1100-1105. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.04.49. PMID: 31179051; PMCID: PMC6531746.
Efficacy and safety profile of roflumilast in a real-world experience
Roflumilast was found to significantly reduce COPD exacerbations and hospitalizations in a real-world setting, with patients experiencing fewer flare-ups and hospital visits compared to the pre-treatment period. However, adverse events, including weight loss, loss of appetite, and nausea, were common and led to a 19.3% discontinuation rate.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31179051/.Tashkin D. P. (2014). Roflumilast : the new orally active, selective phophodiesterase-4 inhibitor, for the treatment of COPD. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy, 15(1), 85–96. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.2013.837159
Roflumilast : the new orally active, selective phophodiesterase-4 inhibitor, for the treatment of COPD
Roflumilast is an orally active, once-daily PDE4 inhibitor approved for COPD patients with chronic bronchitis, severe airflow obstruction, and a history of exacerbations. It reduces exacerbations in patients already using long-acting bronchodilators, although it may cause gastrointestinal side effects and weight loss.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24032576/.Calverley, P. M., Rabe, K. F., Goehring, U. M., Kristiansen, S., Fabbri, L. M., Martinez, F. J., & M2-124 and M2-125 study groups (2009). Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet (London, England), 374(9691), 685–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61255-1.
Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials
Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, significantly improved lung function and reduced the frequency of moderate and severe COPD exacerbations in patients with severe airflow limitation and bronchitic symptoms. In two large trials, roflumilast increased FEV1 and reduced exacerbations compared to placebo, though it was associated with more adverse events, including weight loss.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19716960/.Bardin P, Kanniess F, Gauvreau G, Bredenbröker D, Rabe KF. Roflumilast for asthma: Efficacy findings in mechanism of action studies. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl:S4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Aug 19. PMID: 26296794.
Roflumilast for asthma: Efficacy findings in mechanism of action studies
Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in asthma, similar to its role in COPD. In clinical studies, it reduced allergen-induced bronchoconstriction, inflammation, and airway responses, suggesting potential benefits in asthma treatment, though side effects were consistent with those observed in COPD without significant weight loss.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26296794/.Bateman ED, Izquierdo JL, Harnest U, Hofbauer P, Magyar P, Schmid-Wirlitsch C, Leichtl S, Bredenbröker D. Efficacy and safety of roflumilast in the treatment of asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006 May;96(5):679-86. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61065-4. PMID: 16729780.
Efficacy and safety of roflumilast in the treatment of asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol
Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase type 4 inhibitor, significantly improved lung function (FEV1) and peak expiratory flow in patients with mild-to-moderate asthma, with the 500-microg dose showing the greatest benefit. The treatment was well tolerated, with most side effects being mild to moderate, supporting its potential as an alternative anti-inflammatory therapy for asthma.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16729780/.Chervinsky P, Meltzer EO, Busse W, Ohta K, Bardin P, Bredenbröker D, Bateman ED. Roflumilast for asthma: Safety findings from a pooled analysis of ten clinical studies. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl:S28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Nov 22. PMID: 26612545.
Roflumilast for asthma: Safety findings from a pooled analysis of ten clinical studies
A safety evaluation of roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, in patients with bronchial asthma revealed common adverse events such as headache, gastrointestinal issues (nausea and diarrhea), and mild weight loss, with similar rates in both the treatment and placebo groups. The data, collected from 5169 patients in various global studies, suggests that while roflumilast is generally well-tolerated, it is associated with some gastrointestinal side effects and headaches.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26612545/.Bateman ED, Bousquet J, Aubier M, Bredenbröker D, O’Byrne PM. Roflumilast for asthma: Efficacy findings in non-placebo-controlled comparator and dosing studies. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl:S11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.10.002. Epub 2015 Oct 8. PMID: 26456372.
Roflumilast for asthma: Efficacy findings in non-placebo-controlled comparator and dosing studies
Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, was found to be non-inferior to beclomethasone dipropionate (BDP) and montelukast in improving lung function and asthma symptoms in patients with mild to moderate asthma. The results suggest that roflumilast effectively increases FEV1 and reduces asthma symptoms, warranting further investigation as a potential anti-inflammatory treatment for asthma.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26456372/.Meltzer EO, Chervinsky P, Busse W, Ohta K, Bardin P, Bredenbröker D, Bateman ED. Roflumilast for asthma: Efficacy findings in placebo-controlled studies. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl:S20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Oct 21. PMID: 26498386.
Roflumilast for asthma: Efficacy findings in placebo-controlled studies
Roflumilast has shown potential as an effective anti-inflammatory therapy for asthma, with improvements in FEV1 observed across several placebo-controlled trials. When used in combination with inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), it provided additional benefits, particularly in reducing asthma exacerbations, warranting further investigation into its long-term efficacy.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26498386/Murad HA, Habib HS, Rafeeq MM, Sulaiman MI, Abdulrahman AS, Khabaz MN. Co-inhalation of roflumilast, rather than formoterol, with fluticasone more effectively improves asthma in asthmatic mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Mar;242(5):516-526. doi: 10.1177/1535370216685006. Epub 2017 Jan 5. PMID: 28056550; PMCID: PMC5367656.
Co-inhalation of roflumilast, rather than formoterol, with fluticasone more effectively improves asthma in asthmatic mice
Roflumilast, approved for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), may offer potential off-label benefits for asthma treatment, particularly in cases of eosinophilic and neutrophilic inflammation. This study found that co-inhalation of roflumilast and fluticasone significantly reduced airway hyperresponsiveness and improved inflammation and histopathological changes in ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice, outperforming formoterol and fluticasone in the process.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28056550/.Kim SW, Kim JH, Park CK, Kim TJ, Lee SY, Kim YK, Kwon SS, Rhee CK, Yoon HK. Effect of roflumilast on airway remodelling in a murine model of chronic asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016 May;46(5):754-63. doi: 10.1111/cea.12670. PMID: 26542330.
Effect of roflumilast on airway remodelling in a murine model of chronic asthma
This study investigates the effects of roflumilast on airway inflammation and remodelling in a murine model of chronic asthma. The results show that roflumilast significantly reduced airway inflammation, hyper-responsiveness, goblet cell hyperplasia, and pulmonary fibrosis, with its beneficial effects potentially linked to the SCF/c-kit pathway.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26542330/.Zhang X, Chen Y, Fan L, et al. Pharmacological mechanism of roflumilast in the treatment of asthma-COPD overlap. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:2371-2379. Published 2018 Aug 1. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S165161.
Pharmacological mechanism of roflumilast in the treatment of asthma-COPD overlap
Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, has shown potential in treating asthma-COPD overlap (ACO), but its mechanism remains unclear. A systematic review of its therapeutic action aims to guide clinical decisions, improve diagnosis, and establish treatment guidelines for ACO.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30122895/.Bateman ED, Goehring UM, Richard F, Watz H. Roflumilast combined with montelukast versus montelukast alone as add-on treatment in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Jul;138(1):142-149.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.11.035. Epub 2016 Feb 23. PMID: 26915674.
Roflumilast combined with montelukast versus montelukast alone as add-on treatment in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma
A phase 2 study examined the efficacy of combining roflumilast, a selective PDE4 inhibitor, with montelukast in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. The results showed that the combination significantly improved lung function and asthma control compared to montelukast alone, with improvements in FEV1, patient-reported outcomes, and a reduction in urinary leukotriene E4 levels, suggesting it may be a beneficial treatment option for asthma patients inadequately controlled by standard medications.
You can read the full article at
https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(16)00107-X/.Bousquet J, Aubier M, Sastre J, Izquierdo JL, Adler LM, Hofbauer P, Rost KD, Harnest U, Kroemer B, Albrecht A, Bredenbröker D. Comparison of roflumilast, an oral anti-inflammatory, with beclomethasone dipropionate in the treatment of persistent asthma. Allergy. 2006 Jan;61(1):72-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2005.00931.x. PMID: 16364159.
Comparison of roflumilast, an oral anti-inflammatory, with beclomethasone dipropionate in the treatment of persistent asthma
Roflumilast 500 µg once daily was found to be comparable to inhaled beclomethasone dipropionate (BDP) 400 µg/day in improving lung function, asthma symptoms, and reducing rescue medication use in patients with asthma. Both treatments were well tolerated, with no significant differences in efficacy or clinically relevant improvements between the two.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16364159/.Louw C, Williams Z, Venter L, Leichtl S, Schmid-Wirlitsch C, Bredenbroker D, Bardin PG. Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, reduces airway hyperresponsiveness after allergen challenge. Respiration. 2007;74(4):411-7. doi: 10.1159/000095677. Epub 2006 Sep 5. PMID: 16954654.
Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, reduces airway hyperresponsiveness after allergen challenge
This pilot study evaluated the effects of roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, on allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) in patients with mild asthma. Results showed that roflumilast significantly reduced AHR and attenuated late asthmatic responses to allergen challenge, suggesting its potential as an anti-inflammatory treatment for asthma.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16954654/.Wu Q, Qi L, Li H, Mao L, Yang M, Xie R, Yang X, Wang J, Zhang Z, Kong J, Sun B. Roflumilast Reduces Cerebral Inflammation in a Rat Model of Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Inflammation. 2017 Aug;40(4):1245-1253. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0567-8. PMID: 28451841; PMCID: PMC6193485.
Roflumilast Reduces Cerebral Inflammation in a Rat Model of Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Inflammation
Roflumilast, a selective PDE4 inhibitor, significantly improves neurological deficits and reduces cerebral inflammation in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). It lowers blood-brain barrier permeability, brain edema, and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, highlighting its potential as a treatment for cerebral inflammation following SAH.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6193485/.Feng H, Wang C, He W, Wu X, Li S, Zeng Z, Wei M, He B. Roflumilast ameliorates cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice via cAMP/CREB/BDNF signaling and anti-neuroinflammatory effects. Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Apr;34(2):583-591. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0374-4. Epub 2019 Jan 4. PMID: 30610438.
Roflumilast ameliorates cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice via cAMP/CREB/BDNF signaling and anti-neuroinflammatory effects
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor approved for COPD, improved learning and memory in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model (APP/PS1) by enhancing cognitive function and modulating the cAMP/CREB/BDNF pathway. It also reduced neuroinflammation by decreasing proinflammatory cytokines and inhibiting NF-κB activation in the hippocampus.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30610438/.Vilhena ER, Bonato JM, Schepers M, Kunieda JKC, Milani H, Vanmierlo T, Prickaerts J, de Oliveira RMW. Positive effects of roflumilast on behavior, neuroinflammation, and white matter injury in mice with global cerebral ischemia. Behav Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 1;32(6):459-471. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000640. PMID: 34320520.
Positive effects of roflumilast on behavior, neuroinflammation, and white matter injury in mice with global cerebral ischemia
The study evaluated the effects of the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in a cerebral ischemia model, showing that it prevented cognitive and emotional deficits, reduced neurodegeneration, and decreased white matter damage. Roflumilast’s neuroprotective effects were attributed to its ability to reduce neuroinflammation by modulating microglial markers and inflammatory pathways.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34320520/.Vanmierlo T, Creemers P, Akkerman S, van Duinen M, Sambeth A, De Vry J, Uz T, Blokland A, Prickaerts J. The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses. Behav Brain Res. 2016 Apr 15;303:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.031. Epub 2016 Jan 18. PMID: 26794595.
The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses. Behav Brain Res
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor approved for COPD, has shown promise as a cognition enhancer with minimal emetic side effects compared to rolipram, a classic PDE4 inhibitor. In mice studies, roflumilast improved memory and cognition with significantly lower emetic potential, making it a potentially safer alternative for treating cognitive deficits.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26794595/.Santiago A, Soares LM, Schepers M, Milani H, Vanmierlo T, Prickaerts J, Weffort de Oliveira RM. Roflumilast promotes memory recovery and attenuates white matter injury in aged rats subjected to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Neuropharmacology. 2018 Aug;138:360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.06.019. Epub 2018 Jun 19. PMID: 29933009.
Roflumilast promotes memory recovery and attenuates white matter injury in aged rats subjected to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion
The study evaluated the effects of roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase type 4 inhibitor, on memory and brain injury in aged rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH). Repeated roflumilast treatment improved cognitive performance and reduced white matter injury, suggesting its potential for treating cognitive impairments associated with CCH, despite not rescuing hippocampal neurons.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29933009/.Xu B, Xu J, Cai N, Li M, Liu L, Qin Y, Li X, Wang H. Roflumilast prevents ischemic stroke-induced neuronal damage by restricting GSK3β-mediated oxidative stress and IRE1α/TRAF2/JNK pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Feb 1;163:281-296. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.018. Epub 2020 Dec 24. PMID: 33359910.
Roflumilast prevents ischemic stroke-induced neuronal damage by restricting GSK3β-mediated oxidative stress and IRE1α/TRAF2/JNK pathway
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, has shown potential in protecting neurons from ischemic stroke-associated injury by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis. It works through the activation of GSK3β/Nrf-2 signaling and suppression of the IRE1α/TRAF2/JNK pathway, suggesting its therapeutic potential for treating cerebral ischemia.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33359910/.Wang H, Zhang FF, Xu Y, Fu HR, Wang XD, Wang L, Chen W, Xu XY, Gao YF, Zhang JG, Zhang HT. The Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor Roflumilast, a Potential Treatment for the Comorbidity of Memory Loss and Depression in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preclinical Study in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 Dec 10;23(10):700-711. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa048. PMID: 32645141; PMCID: PMC7727475.
The Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor Roflumilast, a Potential Treatment for the Comorbidity of Memory Loss and Depression in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preclinical Study in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, improves cognitive function and reduces depression-like behavior in AD mice by enhancing cAMP signaling and protecting neurons from apoptosis. These effects suggest roflumilast could be a promising therapeutic agent for Alzheimer’s disease, particularly for addressing both memory loss and depression comorbidity.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32645141/.Hasan N, Zameer S, Najmi AK, Parvez S, Yar MS, Akhtar M. Roflumilast and tadalafil improve learning and memory deficits in intracerebroventricular Aβ1-42 rat model of Alzheimer’s disease through modulations of hippocampal cAMP/cGMP/BDNF signaling pathway. Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Oct;73(5):1287-1302. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00264-w. Epub 2021 Apr 15. PMID: 33860460.
Roflumilast and tadalafil improve learning and memory deficits in intracerebroventricular Aβ1-42 rat model of Alzheimer’s disease through modulations of hippocampal cAMP/cGMP/BDNF signaling pathway
This study explores the therapeutic potential of roflumilast (RFM) and tadalafil (TDF), phosphodiesterase inhibitors, in treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in rats. Both drugs improved memory and reduced neuropathological alterations by upregulating the cAMP/cGMP/BDNF pathway, suggesting their potential as treatments for cognitive deficits associated with AD.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33860460/.Bonato JM, Meyer E, de Mendonça PSB, Milani H, Prickaerts J, Weffort de Oliveira RM. Roflumilast protects against spatial memory impairments and exerts anti-inflammatory effects after transient global cerebral ischemia. Eur J Neurosci. 2021 Feb;53(4):1171-1188. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15089. Epub 2021 Jan 21. PMID: 33340424.
Roflumilast protects against spatial memory impairments and exerts anti-inflammatory effects after transient global cerebral ischemia
The study investigated the effects of the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast on memory loss and neuroinflammation following transient global cerebral ischemia (TGCI) in rats. Repeated roflumilast treatment prevented memory deficits and reduced neuroinflammation, suggesting its protective effects may be linked to anti-inflammatory properties and enhanced neurogenesis in the hippocampus.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33340424/.Gilleen J, Farah Y, Davison C, Kerins S, Valdearenas L, Uz T, Lahu G, Tsai M, Ogrinc F, Reichenberg A, Williams SC, Mehta MA, Shergill SS. An experimental medicine study of the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, roflumilast, on working memory-related brain activity and episodic memory in schizophrenia patients. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 May;238(5):1279-1289. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5134-y. Epub 2018 Dec 8. PMID: 30536081; PMCID: PMC8062361.
An experimental medicine study of the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, roflumilast, on working memory-related brain activity and episodic memory in schizophrenia patients
This study investigated the potential of roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, to improve cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Results showed that roflumilast (250 μg) significantly improved verbal memory, but had no effect on working memory, and reduced dorsolateral prefrontal cortex activation during a working memory task, suggesting PDE4 inhibition may offer a novel approach to treating cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30536081/.Jabaris SG, Sumathy H, Kumar RS, Narayanan S, Thanikachalam S, Babu CS. Effects of rolipram and roflumilast, phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors, on hypertension-induced defects in memory function in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan 5;746:138-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.10.039. Epub 2014 Nov 6. PMID: 25446433.
Effects of rolipram and roflumilast, phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors, on hypertension-induced defects in memory function in rats
Inhibition of PDE-4 with rolipram and roflumilast improved learning and memory impairments in hypertensive rats, as shown by reversal of deficits in the novel object recognition and elevated plus maze tasks. The study also found that PDE-4B and PDE-4D gene expression was upregulated in hypertensive rats, and treatment with PDE-4 inhibitors downregulated these expressions, suggesting a potential therapeutic approach for hypertension-induced cognitive decline.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25446433/.Wang H, Zhang FF, Xu Y, et al. The Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor Roflumilast, a Potential Treatment for the Comorbidity of Memory Loss and Depression in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preclinical Study in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020;23(10):700-711. doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyaa048.
The Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor Roflumilast, a Potential Treatment for the Comorbidity of Memory Loss and Depression in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preclinical Study in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, has been shown to improve cognitive function and reduce depression-like behaviors in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The drug works by modulating the cAMP signaling pathway, alleviating neuronal damage and apoptosis, and may serve as a potential therapeutic for AD, particularly in addressing both memory loss and depression.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32645141/.Keskin H, Keskin F, Tavaci T, Halici H, Yuksel TN, Ozkaraca M, Bilen A, Halici Z. Neuroprotective effect of roflumilast under cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury in juvenile rats through NLRP-mediated inflammatory response inhibition. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2021 Aug;48(8):1103-1110. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13493. Epub 2021 May 10. PMID: 33686709.
Neuroprotective effect of roflumilast under cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury in juvenile rats through NLRP-mediated inflammatory response inhibition. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol
This study investigates the protective effect of roflumilast, a PDE-4 inhibitor, against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (CI/RI) in juvenile rats. The results show that roflumilast treatment significantly reduced inflammatory markers (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and NLRP3) and cellular damage, improving brain tissue health and Nissl body density compared to untreated CI/RI groups, suggesting its potential role in preventing stroke-induced brain damage.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33686709/.Saroj P, Bansal Y, Singh R, Akhtar A, Sodhi RK, Bishnoi M, Sah SP, Kuhad A. Neuroprotective effects of roflumilast against quinolinic acid-induced rat model of Huntington’s disease through inhibition of NF-κB mediated neuroinflammatory markers and activation of cAMP/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Apr;29(2):499-511. doi: 10.1007/s10787-020-00787-3. Epub 2021 Jan 31. PMID: 33517508.
Neuroprotective effects of roflumilast against quinolinic acid-induced rat model of Huntington’s disease through inhibition of NF-κB mediated neuroinflammatory markers and activation of cAMP/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway
Roflumilast shows potential as a therapeutic agent for Huntington’s disease by improving motor function and reducing neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in a quinolinic acid-induced rat model. Its effects are linked to activation of the cAMP/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway and suppression of PDE4 expression.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33517508/.Heckman PRA, Van Duinen MA, Blokland A, Uz T, Prickaerts J, Sambeth A. Acute administration of roflumilast enhances sensory gating in healthy young humans in a randomized trial. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(1):301-308. doi:10.1007/s00213-017-4770-y.
Acute administration of roflumilast enhances sensory gating in healthy young humans in a randomized trial
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, was shown to improve sensory gating in healthy young adults at a low dose (100 μg) without causing side effects. These findings suggest its potential as a treatment for disorders with impaired sensory gating, such as ADHD and schizophrenia.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5748397/.Livingston NR, Hawkins PC, Gilleen J, Ye R, Valdearenas L, Shergill SS, Mehta MA. Preliminary evidence for the phosphodiesterase type-4 inhibitor, roflumilast, in ameliorating cognitive flexibility deficits in patients with schizophrenia. J Psychopharmacol. 2021 Sep;35(9):1099-1110. doi: 10.1177/02698811211000778. Epub 2021 Apr 28. PMID: 33908296; PMCID: PMC8435828.
Preliminary evidence for the phosphodiesterase type-4 inhibitor, roflumilast, in ameliorating cognitive flexibility deficits in patients with schizophrenia
Roflumilast demonstrated dose-dependent cognitive-enhancing effects in patients with schizophrenia, improving performance on tasks involving cognitive flexibility and modulating brain activity in key prefrontal and parietal regions. These findings support further investigation of roflumilast as a potential treatment for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33908296/.Schreiber R, Hollands R, Blokland A. A Mechanistic Rationale for PDE-4 Inhibitors to Treat Residual Cognitive Deficits in Acquired Brain Injury. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(3):188-201. doi: 10.2174/1570159X17666191010103044. PMID: 31660837; PMCID: PMC7327948.
A Mechanistic Rationale for PDE-4 Inhibitors to Treat Residual Cognitive Deficits in Acquired Brain Injury
PDE4 inhibitors like roflumilast may offer a novel treatment for cognitive deficits in acquired brain injury (ABI) by enhancing cAMP signaling, which reduces inflammation and promotes synaptic plasticity. These mechanisms target key consequences of blood-brain barrier breakdown and may improve cognitive outcomes in ABI patients.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7327948/.Heckman PRA, Roig Kuhn F, Raven F, Bolsius YG, Prickaerts J, Meerlo P, Havekes R. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors roflumilast and vardenafil prevent sleep deprivation-induced deficits in spatial pattern separation. Synapse. 2020 Jun;74(6):e22150. doi: 10.1002/syn.22150. Epub 2020 Mar 3. PMID: 32056276.
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors roflumilast and vardenafil prevent sleep deprivation-induced deficits in spatial pattern separation
Sleep deprivation impairs spatial pattern separation in mice by affecting the dentate gyrus, but this deficit can be prevented with PDE inhibitors like roflumilast and vardenafil. These findings suggest potential clinical use of PDE inhibitors to counteract memory deficits caused by sleep loss.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32056276/.Muo IM, MacDonald SD, Madan R, Park SJ, Gharib AM, Martinez PE, Walter MF, Yang SB, Rodante JA, Courville AB, Walter PJ, Cai H, Glicksman M, Guerrieri GM, Ben-Dor RR, Ouwerkerk R, Mao S, Chung JH. Early effects of roflumilast on insulin sensitivity in adults with prediabetes and overweight/obesity involve age-associated fat mass loss – results of an exploratory study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 May 27;12:743-759. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S182953. PMID: 31213865; PMCID: PMC6542328.
Early effects of roflumilast on insulin sensitivity in adults with prediabetes and overweight/obesity involve age-associated fat mass loss – results of an exploratory study
Roflumilast may indirectly improve insulin sensitivity in adults with prediabetes and obesity by promoting fat loss and altering lipid metabolism, with effects becoming more pronounced with age. The study found novel associations between roflumilast-induced changes in incretin hormones, inflammation, and body composition, although most outcomes did not reach statistical significance.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31213865/.Möllmann J, Kahles F, Lebherz C, Kappel B, Baeck C, Tacke F, Werner C, Federici M, Marx N, Lehrke M. The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast reduces weight gain by increasing energy expenditure and leads to improved glucose metabolism. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Apr;19(4):496-508. doi: 10.1111/dom.12839. Epub 2017 Feb 22. PMID: 27917591.
The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast reduces weight gain by increasing energy expenditure and leads to improved glucose metabolism
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, significantly reduced body weight gain, improved glucose tolerance, and decreased insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice by increasing energy expenditure and enhancing mitochondrial function. These findings suggest its potential as a therapeutic strategy for metabolic disorders like obesity and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27917591/.Xu W, Zhang J, Xiao J. Roflumilast Suppresses Adipogenic Differentiation via AMPK Mediated Pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 7;12:662451. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.662451. PMID: 34163436; PMCID: PMC8215703.
Roflumilast Suppresses Adipogenic Differentiation via AMPK Mediated Pathway
Roflumilast, a selective PDE4 inhibitor, was found to suppress adipogenesis and promote lipolysis by activating AMPK and inhibiting key adipogenic regulators such as PPAR-γ and C/EBPα. This suggests its potential as a therapeutic agent for obesity and related metabolic disorders.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34163436/.Jensterle, M., Salamun, V., Kocjan, T., Vrtacnik Bokal, E., & Janez, A. (2015). Short term monotherapy with GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide or PDE 4 inhibitor roflumilast is superior to metformin in weight loss in obese PCOS women: a pilot randomized study. Journal of ovarian research, 8, 32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-015-0161-3.
Short term monotherapy with GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide or PDE 4 inhibitor roflumilast is superior to metformin in weight loss in obese PCOS women: a pilot randomized study
In a 12-week study of obese women with PCOS, both liraglutide and roflumilast led to significant weight loss compared to metformin. Liraglutide was more effective than metformin in improving body composition, while roflumilast also showed additional hormonal and menstrual benefits.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4506413/.Liu Q, Sun Y, Chen D, Chen K, Huang B, Chen Z. Inhibitory effect of roflumilast on experimental periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2021 Jun 14. doi: 10.1002/JPER.20-0858. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34124777.
Inhibitory effect of roflumilast on experimental periodontitis
This study found that PDE4 expression is elevated in the gingival tissue of patients with periodontitis. In a rat model, the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast reduced alveolar bone loss and inflammation, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic agent for periodontitis.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34124777/.Wouters EF, Bredenbröker D, Teichmann P, Brose M, Rabe KF, Fabbri LM, Göke B. Effect of the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor roflumilast on glucose metabolism in patients with treatment-naive, newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Sep;97(9):E1720-5. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2886. Epub 2012 Jun 20. PMID: 22723325.
Effect of the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor roflumilast on glucose metabolism in patients with treatment-naive, newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus
Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, significantly reduced glycated hemoglobin levels and improved glucose homeostasis in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, independent of COPD. While both roflumilast and placebo groups experienced weight loss, the difference between them was not statistically significant.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22723325/.Vollert S, Kaessner N, Heuser A, Hanauer G, Dieckmann A, Knaack D, Kley HP, Beume R, Weiss-Haljiti C. The glucose-lowering effects of the PDE4 inhibitors roflumilast and roflumilast-N-oxide in db/db mice. Diabetologia. 2012 Oct;55(10):2779-2788. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2632-z. Epub 2012 Jul 13. PMID: 22790061.
The glucose-lowering effects of the PDE4 inhibitors roflumilast and roflumilast-N-oxide in db/db mice. Diabetologia
The study investigates the effects of roflumilast and its metabolite roflumilast-N-oxide on GLP-1 levels and glucose regulation in diabetic db/db mice. The results show that both compounds elevate GLP-1, improve insulin release, and prevent disease progression by reducing blood glucose and HbA1c, with roflumilast-N-oxide demonstrating stronger glucose-lowering effects and better protection of pancreatic islet function.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22790061/.Field S. K. (2011). Roflumilast, a Novel Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor, for COPD Patients with a History of Exacerbations. Clinical medicine insights. Circulatory, respiratory and pulmonary medicine, 5, 57–70. https://doi.org/10.4137/CCRPM.S7049.
Roflumilast, a Novel Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor, for COPD Patients with a History of Exacerbations
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive condition characterized by airflow limitation caused by an abnormal inflammatory response to inhaled irritants, primarily cigarette smoke. The disease involves inflammation and unopposed oxidation, leading to lung damage and increased morbidity and mortality, with significant socioeconomic costs.
You can read the full article at
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3351880/.Tikoo, K., Lodea, S., Karpe, P. A., & Kumar, S. (2014). Calorie restriction mimicking effects of roflumilast prevents diabetic nephropathy. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 450(4), 1581–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.039.
Calorie restriction mimicking effects of roflumilast prevents diabetic nephropathy
This study investigates the effect of roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, in treating type 1 diabetic nephropathy in rats. Roflumilast successfully normalized kidney function, reduced oxidative stress, prevented apoptosis, and restored AMPK and SIRT1 levels, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic option for metabolic disorders like diabetic nephropathy.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25035926/.Wouters, E. F., Bredenbröker, D., Teichmann, P., Brose, M., Rabe, K. F., Fabbri, L. M., & Göke, B. (2012). Effect of the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor roflumilast on glucose metabolism in patients with treatment-naive, newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 97(9), E1720–E1725. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-2886.
Effect of the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor roflumilast on glucose metabolism in patients with treatment-naive, newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus
A study investigating the effects of roflumilast in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (DM2) found that roflumilast significantly reduced glycated hemoglobin levels and improved several metabolic parameters, including glucose and free fatty acids. While both the roflumilast and placebo groups experienced weight loss, the difference between the two was not statistically significant, indicating roflumilast may positively impact glucose homeostasis in DM2 patients.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22723325/-
You can read the abstract of this article at
Ding H, Zhang P, Li N, Liu Y, Wang P. The phosphodiesterase type 4 inhibitor roflumilast suppresses inflammation to improve diabetic bladder dysfunction rats. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Feb;51(2):253-260. doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-2038-z. Epub 2018 Nov 24. PMID: 30474782.
The phosphodiesterase type 4 inhibitor roflumilast suppresses inflammation to improve diabetic bladder dysfunction rats
A study demonstrated that roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase type 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, improves bladder function and reduces inflammation in diabetic bladder dysfunction (DBD) in diabetic rats. The treatment attenuated the expression of inflammatory factors in detrusor smooth muscle, suggesting PDE4 as a potential therapeutic target for DBD.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30474782/.Ding H, Li N, He X, Liu B, Dong L, Liu Y. Treatment of obesity-associated overactive bladder by the phosphodiesterase type-4 inhibitor roflumilast. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017 Oct;49(10):1723-1730. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1671-2. Epub 2017 Jul 29. PMID: 28756610.
Treatment of obesity-associated overactive bladder by the phosphodiesterase type-4 inhibitor roflumilastThis study investigates the potential of phosphodiesterase type-4 inhibitor roflumilast in treating obesity-associated overactive bladder by modulating the systemic inflammatory response. The results show that roflumilast treatment in high-fat diet-fed rats restored normal bladder function and reduced inflammatory markers, although it did not affect body weight.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28756610/.Yeo CD, Kim YA, Lee HY, Kim JW, Kim SJ, Lee SH, Kim YK. Roflumilast treatment inhibits lung carcinogenesis in benzo(a)pyrene-induced murine lung cancer model. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 5;812:189-195. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 4. PMID: 28684234.
Roflumilast treatment inhibits lung carcinogenesis in benzo(a)pyrene-induced murine lung cancer model
Roflumilast, a selective PDE4 inhibitor, has shown potential in reducing lung carcinogenesis in a B(a)P-induced murine model. Treatment with a high dose of roflumilast (5mg/kg) decreased tumor load, increased cAMP levels, and reduced markers of inflammation and angiogenesis, suggesting its chemopreventive effect in lung cancer.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28684234/.Gong S, Chen Y, Meng F, Zhang Y, Wu H, Wu F. Roflumilast restores cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling axis for FtMt-mediated tumor inhibition of ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(68):112341-112353. Published 2017 Dec 2. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.22866.
Roflumilast restores cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling axis for FtMt-mediated tumor inhibition of ovarian cancer
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, demonstrates potential anti-cancer effects in ovarian cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and promoting cell cycle arrest. It activates the cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway, up-regulating mitochondrial ferritin (FtMt) expression, which enhances apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth in ovarian cancer cell lines and in vivo.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29348829/.Domvri K, Zarogoulidis K, Zogas N, Zarogoulidis P, Petanidis S, Porpodis K, Kioseoglou E, Hohenforst-Schmidt W. Potential synergistic effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors with chemotherapy in lung cancer. J Cancer. 2017 Oct 9;8(18):3648-3656. doi: 10.7150/jca.21783. PMID: 29151951; PMCID: PMC5688917.
Potential synergistic effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors with chemotherapy in lung cancer
This study explores the potential anti-tumor effects of combining methylxanthines (theophylline) and phosphodiesterase inhibitors (roflumilast and sildenafil) with chemotherapeutic agents in lung cancer. The results show that these combinations, particularly with carboplatin and cisplatin, enhanced apoptosis in small cell and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines, suggesting they could be beneficial as additive or maintenance treatments in lung cancer therapy.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29151951/.Kim, D. Y., Nam, J., Chung, J. S., Kim, S. W., & Shin, H. J. (2022). Role of Roflumilast Combined with ESHAP Chemotherapy in Relapsed/Refractory Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancer research and treatment, 54(1), 301–313. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2020.1371.
Role of Roflumilast Combined with ESHAP Chemotherapy in Relapsed/Refractory Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
The study explores the synergistic effects of phosphodiesterase inhibitors (roflumilast, sildenafil, and theophylline) combined with chemotherapeutic agents (cisplatin, carboplatin, and docetaxel) in treating lung cancer. Results showed increased apoptosis and cytotoxicity in small cell and non-small cell lung cancer cells, suggesting these combinations could be promising as additive and maintenance treatments for lung cancer patients.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5688917/.Gong, S., Chen, Y., Meng, F., Zhang, Y., Li, C., Zhang, G., Huan, W., & Wu, F. (2018). Roflumilast enhances cisplatin-sensitivity and reverses cisplatin-resistance of ovarian cancer cells via cAMP/PKA/CREB-FtMt signalling axis. Cell proliferation, 51(5), e12474. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12474.
Roflumilast enhances cisplatin-sensitivity and reverses cisplatin-resistance of ovarian cancer cells via cAMP/PKA/CREB-FtMt signalling axis
This study investigated roflumilast’s role in enhancing cisplatin (DDP) sensitivity and reversing DDP resistance in ovarian cancer. The results showed that roflumilast, through the activation of the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway and upregulation of FtMt expression, inhibited cell proliferation, induced apoptosis, and sensitized both DDP-sensitive and -resistant ovarian cancer cells, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic strategy in ovarian cancer treatment.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30069985/.Abdel-Wahab, B. A., Walbi, I. A., Albarqi, H. A., Ali, F., & Hassanein, E. (2021). Roflumilast protects from cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity in male rats and enhances its cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cell line. Role of NF-κB-p65, cAMP/PKA and Nrf2/HO-1, NQO1 signaling. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 151, 112133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112133.
Roflumilast protects from cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity in male rats and enhances its cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cell line
This study investigates the protective effects of roflumilast (ROF), a PDE4 inhibitor, against cisplatin (CIS)-induced testicular injury in rats, showing that ROF alleviates sperm abnormalities, normalizes testosterone levels, and improves testicular structure by modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis pathways. Additionally, ROF enhances CIS’s anticancer effects in vitro by increasing the expression of Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO-1 while inhibiting NF-κβ, offering a potential therapeutic approach for mitigating CIS-induced testicular toxicity.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33757793/.Saeedan, A. S., Rastogi, S., & Ansari, M. N. (2020). Roflumilast counteracts DMH-induced preneoplastic colon damage in albino Wistar rats. Human & experimental toxicology, 39(11), 1545–1555. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120931165.
Roflumilast counteracts DMH-induced preneoplastic colon damage in albino Wistar rats
The study investigated the chemoprophylactic potential of roflumilast against preneoplastic colon damage induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine (DMH) in rats. Results showed that roflumilast reduced oxidative stress, inflammatory markers, and improved heart rate variability, helping restore normal colonic tissue architecture and mitigating DMH-induced preneoplastic damage.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32524861/.Kelly, K., Mejia, A., Suhasini, A. N., Lin, A. P., Kuhn, J., Karnad, A. B., Weitman, S., & Aguiar, R. C. (2017). Safety and Pharmacodynamics of the PDE4 Inhibitor Roflumilast in Advanced B-cell Malignancies. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, 23(5), 1186–1192. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1207.
Safety and Pharmacodynamics of the PDE4 Inhibitor Roflumilast in Advanced B-cell Malignancies
This study explored the use of the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in combination with prednisone for treating advanced B-cell malignancies. The results showed that roflumilast was safe, effectively suppressed PI3K/AKT activity in 77% of patients, and led to partial responses or stable disease in 66% of evaluable patients, suggesting potential clinical activity in this setting.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27542768/.Ren, H., Chen, Y., Ao, Z., Cheng, Q., Yang, X., Tao, H., Zhao, L., Shen, A., Li, P., & Fu, Q. (2022). PDE4D binds and interacts with YAP to cooperatively promote HCC progression. Cancer letters, 541, 215749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215749.
PDE4D binds and interacts with YAP to cooperatively promote HCC progression
This study explores the role of phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), showing that its overexpression promotes HCC growth by interacting with yes-associated protein (YAP). Targeting this interaction with roflumilast, a PDE4D inhibitor, suppresses YAP activity, leading to reduced HCC cell growth, indicating that PDE4D-YAP inhibition may be a promising therapeutic strategy for HCC.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35597479/.Liu, X., Hao, P. D., Yang, M. F., Sun, J. Y., Mao, L. L., Fan, C. D., Zhang, Z. Y., Li, D. W., Yang, X. Y., Sun, B. L., & Zhang, H. T. (2017). The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor roflumilast decreases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology, 234(16), 2409–2419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4631-8.
The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor roflumilast decreases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice
Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, was found to reduce ethanol intake and preference in C57BL/6J mice in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting its potential as a treatment for alcohol use disorders. The study showed that roflumilast decreased alcohol consumption without affecting natural reward or aversive stimuli, providing novel insights into its role in managing alcoholism.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28477089/.Liu, X., Hao, P. D., Yang, M. F., Sun, J. Y., Mao, L. L., Fan, C. D., Zhang, Z. Y., Li, D. W., Yang, X. Y., Sun, B. L., & Zhang, H. T. (2017). The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor roflumilast decreases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology, 234(16), 2409–2419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4631-8.
The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor roflumilast decreases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice
The study investigates the effects of roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, on ethanol intake and preference in mice, finding that it reduces alcohol consumption in a dose-dependent manner, similar to the positive control rolipram. These results suggest that roflumilast may be beneficial in treating alcohol use disorders by modulating cAMP signaling without affecting natural reward preferences or aversive stimuli.
You can read the abstract of this article at
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28477089/.
Patient Success Stories

Before
After

At the age of 60, I look and feel better than I ever have in my entire life! Switching my health program and hormone replacement therapy regimen over to Genemedics was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made in my life! Genemedics and Dr George have significantly improved my quality of life and also dramatically improved my overall health.
Nick Cassavetes ,60 yrs old Movie Director (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer

Before
After

I am now in my mid-sixties and feel better than I did in my 20’s. Many people have commented that I actually look 20 years younger since I started the program at Genemedics. Calling Dr. George has proven to be one of the best decisions I have made in my life. Doctors and society convince us that developing various health issues and negative sy...
Pamela Hill ,66 yrs old Actress (“The Notebook”, “John Q”, “Alpha Dog”), Actor and Writer
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have
Free Consultation
Start Your Journey to a Younger, Healthier You!
Categories
Information
Free Consultation
STEPS AWAY FROM A YOUNGER. HEALTHIER YOU!
Call 800-277-4041 for a Free Consultation
What to expect during your consultation:
- Usually takes 15-30 minutes
- Completely confidential
- No obligation to purchase anything
- We will discuss your symptoms along with your health and fitness goals
- Free post-consult access for any additional questions you may have








